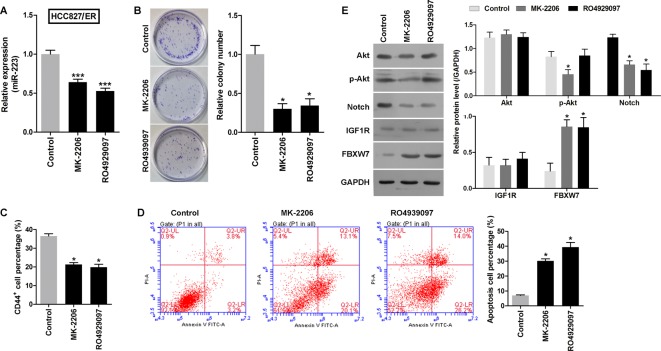
Figure 2. Akt and Notch signaling pathways and miR-223 in HCC827/ER cells.
The levels of miR-223 in HCC827/ER cells were regulated by the Akt and Notch signaling pathways, and inhibition of those pathways reversed chemoresistance to erlotinib. (A) The levels of miR-223 in HCC827/ER cells during their treatment with MK-2206 (an Akt inhibitor) or RO4929097 (a Notch inhibitor) for 48 h, as analyzed by q-PCR. (B) Images recorded with a MicroView imager showing the number of colonies formed by each population of cells. (C) The percentage of CD44+ cells in each group of HCC827/ER cells during 48 h of treatment with MK-2206 (an Akt inhibitor) or RO4929097 (a Notch inhibitor). (D) Representative data from FACS analyses of cell apoptosis levels, and the percentage of apoptotic cells in each group of HCC827/ER cells during 48 h of treatment with MK-2206 (an Akt inhibitor) or RO4929097 (a Notch inhibitor). (E) Western blots showing expression of p-Akt, Akt, Notch, IGF1R, and FBXW7 in HCC827/ER cells treated with MK-2206 (an Akt inhibitor) or RO4929097 (a Notch inhibitor). GAPDH served as an internal control. All data represent the mean value ± SD from three independent experiments; *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001.