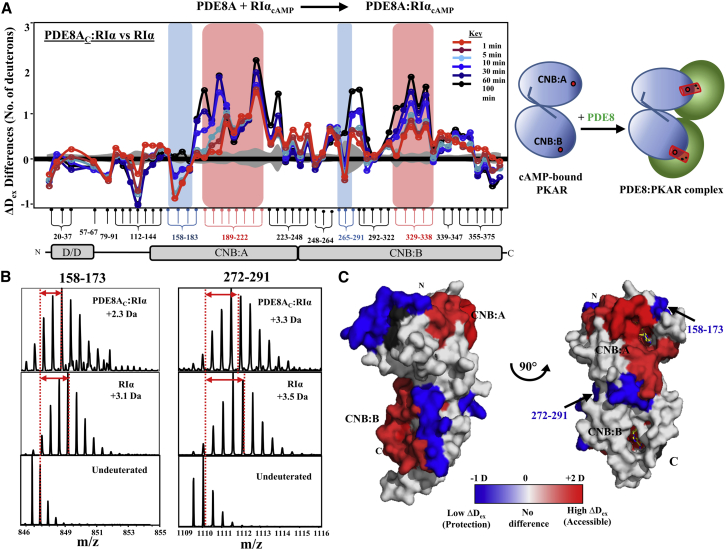
Figure 5.
PDE8-PKA-RIα interaction interface on cAMP-bound RIα. (A) Differences in average deuterons exchanged (Y-axis) in PDE8AC-RIα relative to cAMP-bound RIα for each pepsin fragment peptide listed from N to C terminus (X-axis). Peptides spanning continuous regions are grouped by brace brackets. Peptides spanning the cAMP binding regions in CNB:A (189–222) and CNB:B (329–338) are highlighted in red and peptides specific to PDE8AC binding are in blue. Positive and negative differences in deuterium exchange represent increased and decreased exchange respectively in the PDE8AC-RIα complex. Deuterium exchange times for every peptide are depicted and colored according to key. Standard deviations are shaded gray. Plots were generated using DynamX 2.0 software (Waters, Milford, MA). Cartoon representation of two domains of RIα in blue, connected by a linker; cAMP as red spheres; PDE8 dimer in green, forming a PDE8AC-RIα complex (right). (B) Stacked mass spectra for RIα and PDE8AC-RIα binary complex after 10 min deuterium labeling are shown for the two putative PDE8-binding peptides. Average deuterons exchanged indicated by centroid obtained by calculating the differences between the deuterated and undeuterated peptide centroids (red arrows). (C) Significant differences in deuterium exchange in the binary complex compared to RIα are mapped onto the structure of RIα (PDB: 1RGS (39)) represented in surface in two different orientations. Regions showing increased exchange after 10 min of deuterium labeling are colored in shades of red and regions with decreased exchange in blue. cAMP molecules are shown as yellow sticks. No-coverage regions are in gray.