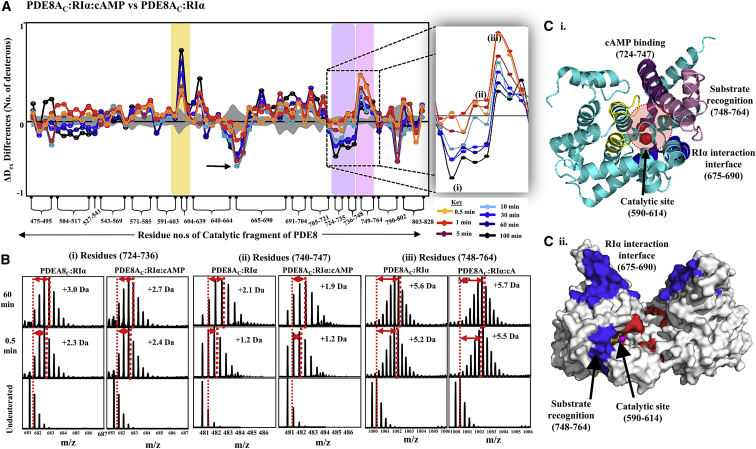
Figure 8.
Enhanced hydrolysis by cAMP translocation in the PDE8-PKA-RIα complex. (A) Plot of the average differences in deuterium uptake (Y axis) between PDE8AC-RIα-cAMP and PDE8AC-RIα, with residue numbers for pepsin fragment peptides of the PDE8A catalytic domain listed from the N- to the C-terminus (X axis). Positive changes denote increased deuterium exchange and negative changes denote decreased exchange in the PDE8AC-RIα complex in excess cAMP. Peptides spanning the catalytic site of PDE8A are highlighted in yellow, substrate binding sites in purple, and the PDE substrate recognition site peptides in pink. Standard deviations are shaded gray. The inset shows a magnification of the three peptides that interact with cAMP, spanning residues 724–736 (i), 740–747 (ii), and 748–764 (iii). (B) Stacked spectral plots for the three peptides (i–iii) are shown for the PDE8AC-RIα complex without and with cAMP, as indicated for different deuterium labeling times. The shifts in centroid values are represented by double-headed arrows. (C) (i) Crystal structure of the monomer of the PDE8A catalytic domain (PDB: 3ECN (32)) depicting the catalytic site in yellow (highlighted with two metal ions in red), cAMP binding sites in purple, the substrate recognition site in pink, and the RIα binding site in blue. (ii) Differences in deuterium exchange observed for PDE8AC-RIα are mapped onto the surface representation of the monomer of PDE8AC, with regions showing decreased exchange in blue and regions with increased exchange in red. To see this figure in color, go online.