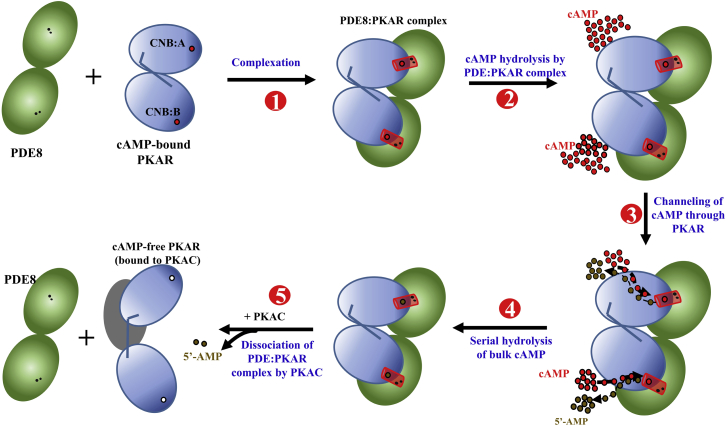
Figure 9.
Processive hydrolysis of cAMP by channeling through the PDE8-PKAR complex. A PDE8 dimer (green circles) binds the cAMP (red circles)-bound PKA regulatory subunit (blue), forming a PDE8-PKAR complex (step 1), bringing the cAMP binding site of PKAR in close proximity to the PDE8 active site (two catalytic metal cations (black dots)) to form a “channel” (red cylinder). This channel drives hydrolysis of the cAMP flux by facilitating translocation of cAMP via PKAR (step 2), resulting in enhanced serial hydrolysis of cAMP (step 3) followed by release of the 5′-AMP product (step 4), until all cAMP molecules are hydrolyzed by the PDE8-PKAR complex. Entry of the C-subunit at this stage (step 5) promotes PKA holoenzyme formation by PDE dissociation and resets cAMP signaling for a new activation/termination cycle. To see this figure in color, go online.