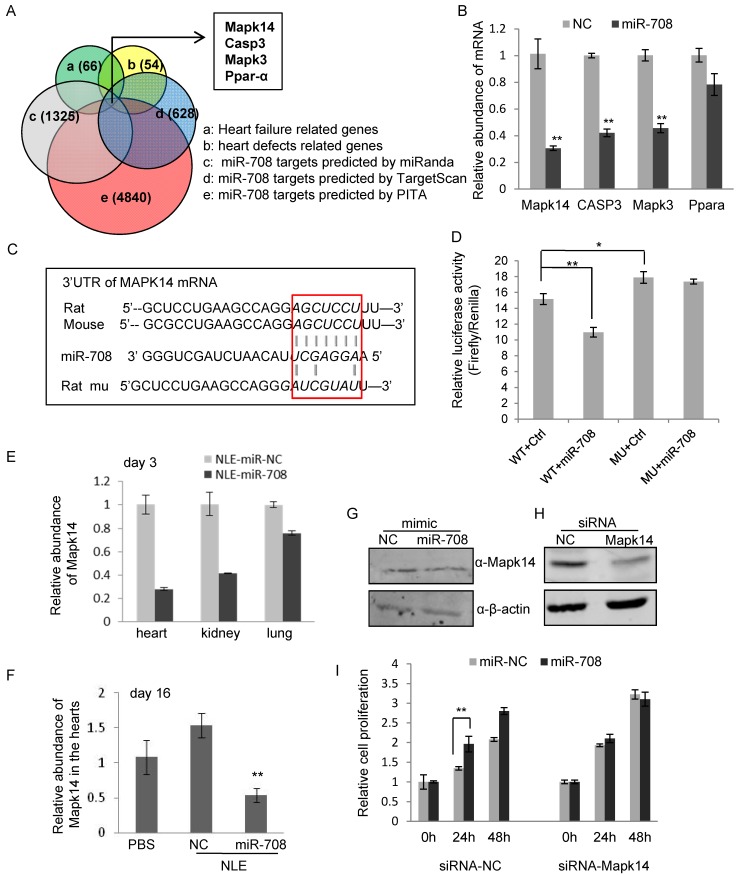
Figure 6.
miR-708 regulates Mapk14 expression in cardiomyocytes. A: Bioinformatics screening using TargetScan, miRanda and PITA predicted miR-708 target genes, which overlapped with 66 heart failure related genes and 54 heart defects related genes, deriving Mapk14, Casp3, Mapk3 and Ppar-α as candidate target genes of miR-708 in rat cardiomyocytes. B: Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analyses demonstrated the decrease of mRNA levels of Mapk14, Casp3 and Mapk3 by miR-708 overexpression in the primary cardiomyocytes isolated from the newborn rats. C: Sequences for the WT and point mutated MAPK14 3'UTR. D: Luciferase reporter assays demonstrated the inhibition of MAKP14 3'UTR by direct interaction with miR-708. E: Decreased MAPK14 levels in the hearts, kidneys and lungs of mice upon miR-708 delivery in vivo after three days' miR-708 treatment. F: Decreased MAPK14 levels in the hearts of NLE-miR-708 treated mice at day 16. G: Western blot analyses demonstrating the decrease of Mapk14 protein level by miR-708 in cardiomyocytes. ß-actin served as loading control. H: Western blot analyses demonstrating the knockdown of Mapk14 by siRNA in H9C2 cells. ß-actin served as loading control. I: MTT analyses showed the increase of cell proliferation by miR-708 only in control H9C2 cells, but not in Mapk14 siRNA treated cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.