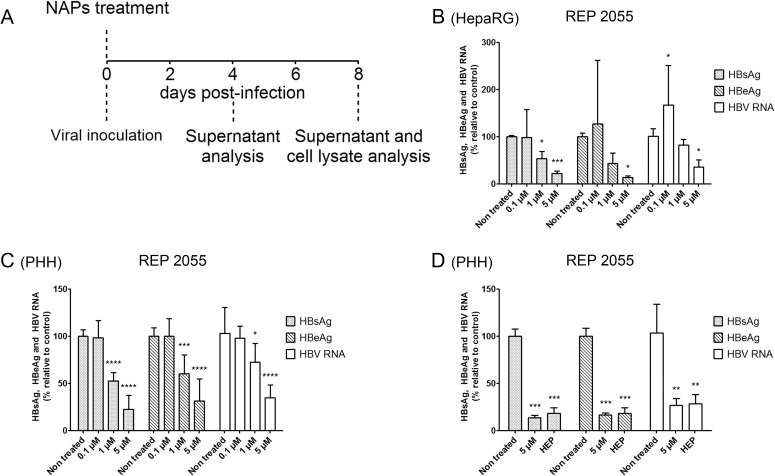
Fig 3. Effect of a single nucleic acid polymers treatment at the time of viral inoculation on HBV replication in HepaRG cells and primary human hepatocytes.
(A) Treatments procedure: HBV infected cells were treated at the time of inoculation for the duration of inoculation with REP 2055 at 0.1 μM, 1 μM and 5 μM final concentrations in (B) differentiated HepaRG cells and (C) primary human hepatocytes at day 8 post-inoculation by measuring secreted HBsAg, HBeAg and total HBV RNA. (D) In primary human hepatocytes, in a side by side experiment with 5 μM REP 2055, heparin (HEP) was used as a positive control for entry inhibition at a concentration of 300 μg/ml (See legend to Fig 1. for experimental details). All data originate from three independent experiments except in (D) where two independent experiments have been performed. Results are expressed as means ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was conducted with R software using an (B, C) ordinary one-way ANOVA with random effect for comparison to non-treated sample and (D) unpaired, 2-tailed t-tests for comparison of specific samples using GraphPadPrism6 software; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.