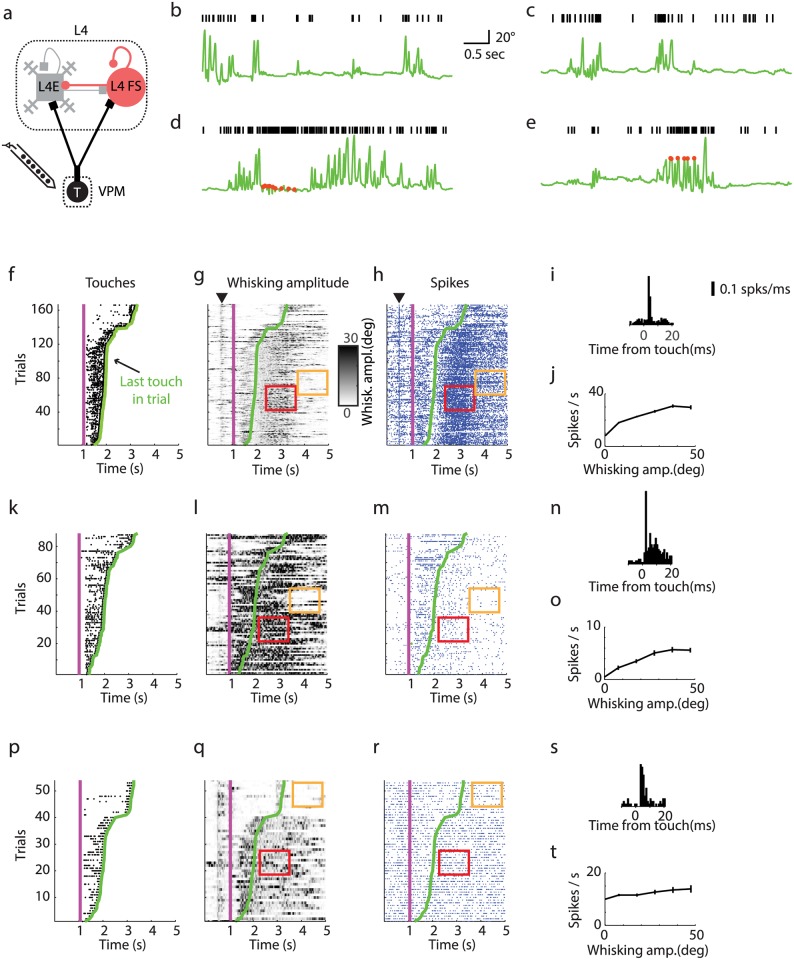
Fig 2. Example neurons recorded in VPM during whisker-based object localization.
(a) Chronic silicon probe recordings in VPM. (b,c) Two example trials from the same neuron showing increases in activity with whisker movements without touch. Green line, whisker azimuthal angle. Black ticks, spikes. (d,e) Two example trials showing increases in spike rate after touch. (f) Touch rasters (black dots; sorted by last touch in a trial). The magenta line shows when the pole was moved within reach of the whiskers. The green line represents the last touch in each trial. (g) Whisker movement amplitude. Red rectangle, epoch of high whisker movement amplitude and high spike rate (same as in h). Orange rectangle, epoch of low amplitude and low spike rate (same as in h). (h) Spike raster for an example neuron in VPM (blue dots, spikes). The black arrow in g-h indicates onset of whisker twitching [52]. The twitching is triggered by an auditory signal generated by the brief activation of a shutter. (i) Peri-stimulus-time-histogram (PSTH) showing response for touch. (j) Spike rate as a function of whisker movement amplitude. (k-o) Same as f-j for another example VPM neuron with low baseline spike rate. (p-t) Same as f-j for another example VPM neuron that does not show modulation with whisking amplitude.