Figure 7.
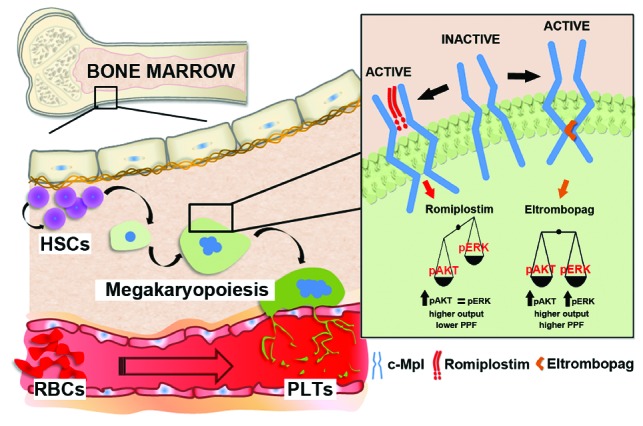
Representative model of different mechanisms of action of eltrombopag and romiplostim. Bone marrow, contained in spongy bones, is a tridimensional network of branching sinusoids surrounding islets of hematopoietic cells. Within this environment hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) undergo self-renewal as well as differentiation into committed lineages in order to support the physiological homeostasis of all blood cells. Megakaryopoiesis takes place due to the activation of c-Mpl, the thrombopoietin receptor, which promotes HSC commitment and differentiation. Upon c-Mpl binding, eltrombopag promotes higher phosphorylation of both AKT and ERK than recombinant human thrombopoietin (rHuTPO), thus ensuring proper proplatelet formation (PPF). At variance with eltrombopag, romiplostim promotes increased AKT but not ERK activation with respect to rHuTPO, thus promoting megakaryocyte proliferation rather than PPF. PLTs: platelets; RBCs: red blood cells.
