Fig. 2. Structural and functional characterization of the DesAbs.
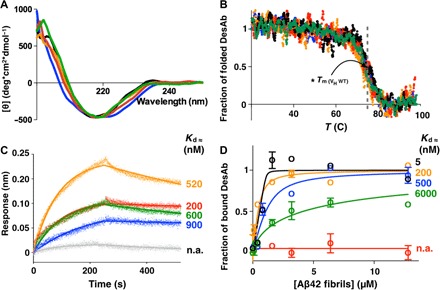
CD spectra (A) and CD thermal denaturation (B) of the DesAbs used in this work. WT, wild type. (B) Denaturation data are reported as fraction of the folded protein (see Materials and Methods). (C) BLI measurements of the binding of the DesAbs to SA sensor chip coated with monomeric biotinylated Aβ42. Each curve was subtracted from a curve of binding of the corresponding DesAb to an uncoated sensor chip; the Kd values of binding to monomeric Aβ42 are reported. Given the proximity of the target peptide of DesAb3–9 to the biosensor surface, the affinity of DesAb3–9 for monomeric Aβ42 was determined with biotin-mediated affinity measurements (fig. S3). n.a., not applicable. (D) Fibril binding experiments of the DesAbs; the Kd values of binding to fibrillar Aβ42 are reported. DesAb3–9, black; DesAb13–19, orange; DesAb18–25, blue; DesAb29–36, green; DesAb36–42, red; DesAb-F (a DesAb that targets α-synuclein), gray. The gray dashed line in (B) indicates the Tm (≈73°C) of the original scaffold as reported in the literature (48).
