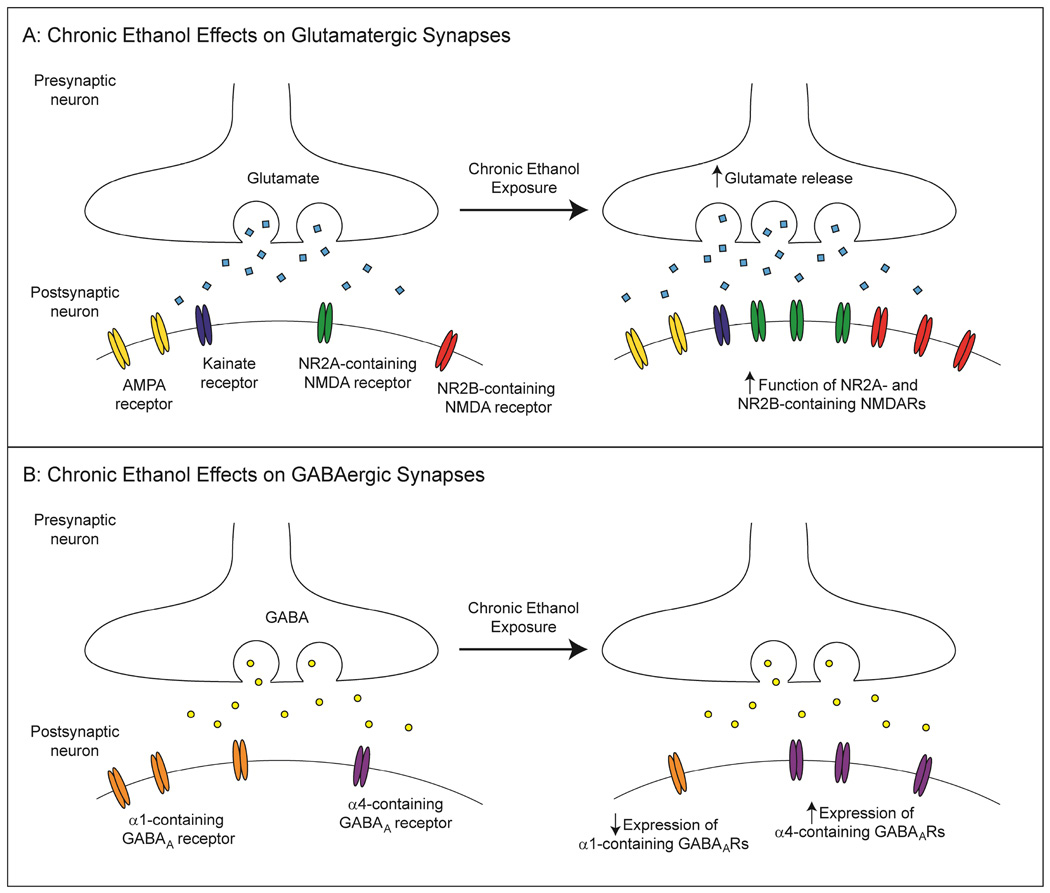
Figure 1.
Chronic ethanol effects on glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission. A: Schematic illustration of a glutamatergic synapse after chronic ethanol exposure. Presynaptically, glutamate release is enhanced. Postsynaptically, NMDAR function is increased, likely due to increased receptor expression. AMPA and kainite receptor function can also be enhanced by chronic ethanol, though these effects tend to be less consistent. B: A GABAergic synapse after chronic ethanol exposure. Presynaptically, GABA release is altered in a brain region-specific manner, potentially due to changes in GABABR function. Postsynaptically, GABAAR composition is altered by chronic ethanol, such that there is an increase in synaptic α4-containing receptor expression and a concomitant decrease in synaptic α1-containing receptor number, though the functional outcome of these changes is less clear.