Figure 1.
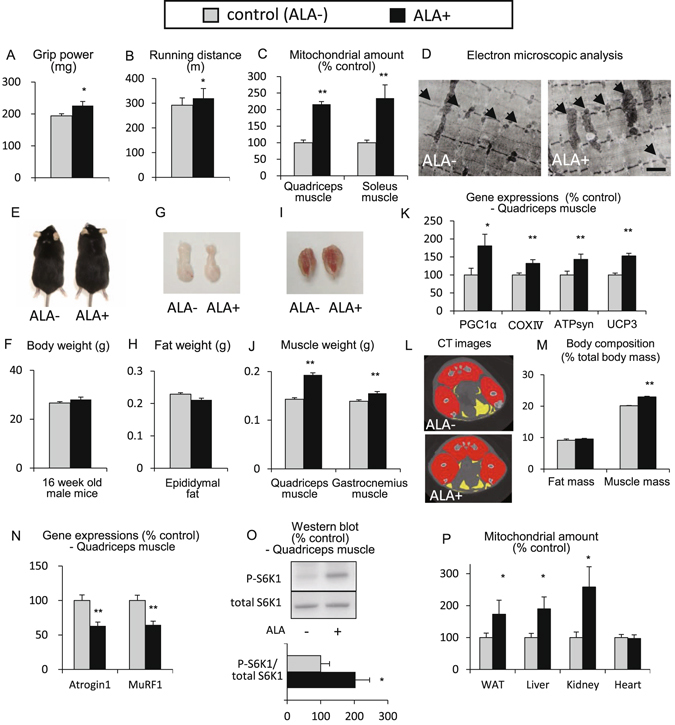
5-aminolevulinic acid improves physical performance by activating mitochondria and increasing muscle mass. To investigate the effects of ALA on muscle mitochondria and physical performance, C57BL/6 mice were fed with an ALA-containing diet (0.03% ALA) for 8 weeks from 8 weeks of age. Control mice (ALA−) and ALA-treated mice (ALA+) were examined. (A) Grip power at 16 weeks (16 W) of age as an index of muscle strength, (B) Running distance at 16 W as an index of endurance, (C) Mitochondrial amount in the quadriceps muscle and soleus muscle, estimated from mitochondrial DNA copy number, (D) Electron microscopic analysis of the quadriceps muscle. Scale bar = 1 µm, (E,G and I) Macroscopic view of the mice, epididymal fat and gastrocnemius muscle with soleus muscle, (F,H and J) The body weight, weight of the epididymal fat, and weight of the quadriceps and gastrocnemius muscle, (K) expression of mitochondria-related genes estimated by quantitative PCR analysis (PGC1α, COXIV, ATPsyn and UCP3), (L) Micro-CT images at the level of the maximal thigh circumference of the mice. The red part is the muscle, the yellow part is the fat, (M) The body composition of the ALA-treated mice at the total body level. The ratios of fat mass and muscle mass to total body volume estimated from the micro-CT images are shown; N = 4 in each group, (N) expression of muscle degradation-related genes estimated by quantitative PCR analysis (Atrogin1, MuRF1), (O) Western blots of P-S6K1 and total S6K1 (upper) and densitometry of the ratio of P-S6K1/total S6K1, as an index of S6K1 activity (lower). Full-length blots are included in the Supplementary Information, (P) Mitochondrial amount in various tissues (WAT, liver, kidney and heart). N = 8 in each group unless otherwise indicated. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control mice. ALA, 5-aminolevlinic acid; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- coactivator 1; COXIV, cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV; ATPsyn, adenosine triphosphate synthase; UCP3, uncoupling protein 3; CT, computed tomography; Murf1, muscle specific ring finger protein 1; P-S6K1, phosphorylated S6 kinase1; WAT, white adipose tissue.
