Figure 1.
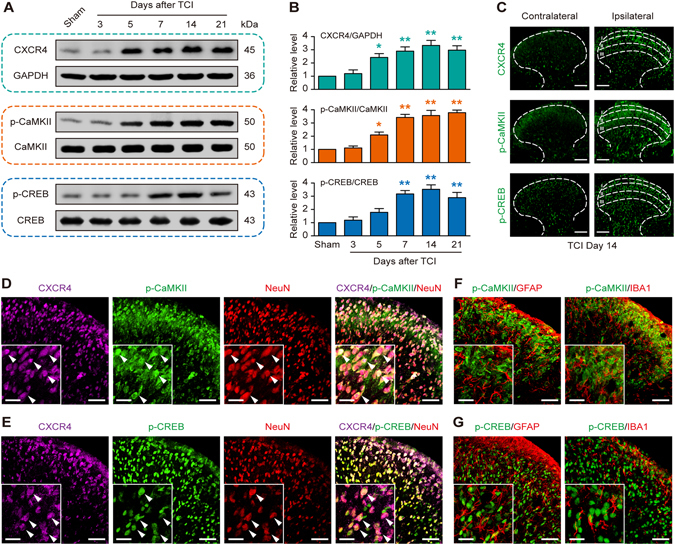
TCI increases the expression and co-localization of CXCR4, p-CaMKII and p-CREB in rat spinal dorsal neurons. (A and B) Western blot showing the time course of CXCR4 (top row), p-CaMKII (middle row) and p-CREB (bottom row) expression after TCI. (A) representative bands; (B) quantitative data. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs sham group; n = 4 for each group. (C) Immunofluorescence staining showing the expression and distribution of CXCR4 (top row), p-CaMKII (middle row) and p-CREB (bottom row) in the spinal cord dorsal horn. (D–G) Double and triple immunofluorescence staining showing cellular co-localization of CXCR4, p-CaMKII/p-CREB and cell markers in TCI rat spinal cord. CXCR4 (violet) co-localized with p-CaMKII (green, D) and p-CREB (green, E) in neurons (NeuN, red). Meanwhile, p-CaMKII (green, F) and p-CREB (green, G) did not co-express with astrocytes (GFAP, red) or microglial cells (IBA1, red). L4-L6 spinal tissues were taken on day 14 after TCI. Original magnification: 200× (C), 400× (D–G), and 1600 × (inserts in D–G); scale bar: 100 μm (C), 50 μm (D–G), and 20 μm (inserts in D–G).
