Figure 4.
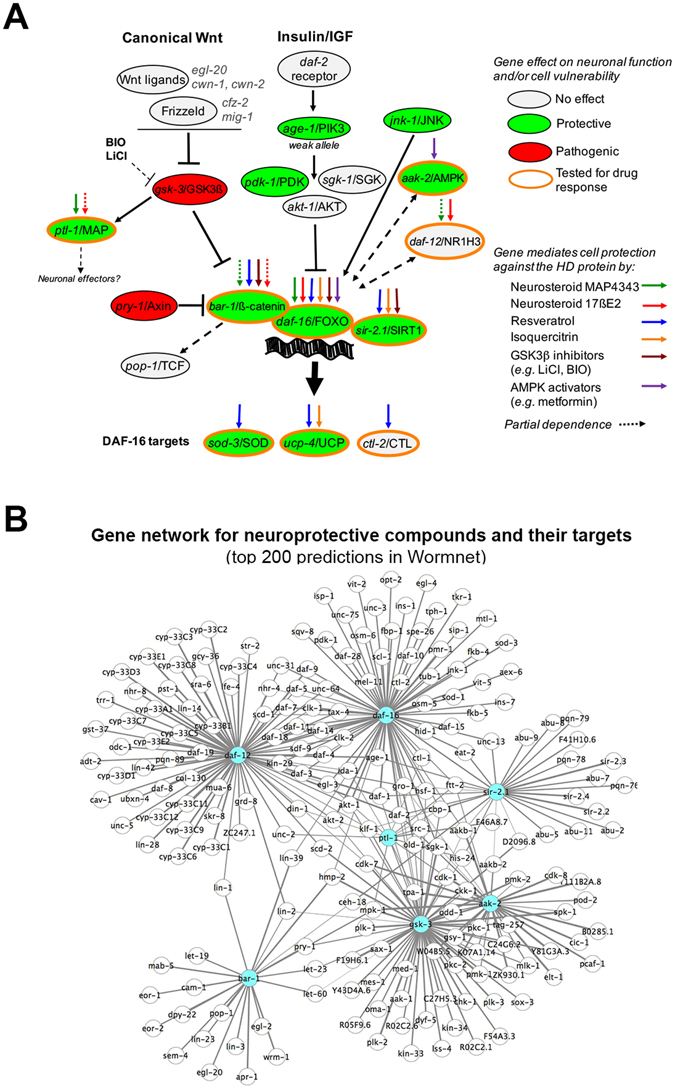
Current model for selective compound families to promote neuronal compensation in HD via a stress response system centered onto FOXO and its co-factors. This model is relevant to the early phases of mutant huntingtin cytoxicity, when neurons and cells are vulnerable but remain functional, and before they undergo degeneration. (A) Pathway layout that results from the synthesis of C. elegans (response to light touch mediated by PLM neurons) and/or mouse striatal cell (mortality induced by serum deprivation) data as reported herein for neurosteroids, resveratrol and isoquercitrin or elsewhere for resveratrol and metformin6, 23. Also included are C. elegans data on the effects of LOF mutants of genes in the canonical Wnt and insulin/IGF pathways (see Fig. S3). Ptl-1/MAP signaling is poorly understood, possibly involving intestinal skn-1 for the regulation of stress response at the organismal level99. (B) Resource networks for investigating neuronal compensation mechanisms used by compounds shown in (A). The figure shows a sub-network of top 200 genes strongly predicted by Wormnet to interact with one or more of seed genes (shown in blue) including sir-2.1/SIRT1, gsk-3/GSK-3ß, daf-16/FOXO, bar-1/ß-catenin, daf-12/NR1H3, aak-2/AMPK and ptl-1/MAP2. This sub-network is selected from a network of 1267 genes (see Table S2) predicted by Wormnet98 to interact with sir-2.1/SIRT1, gsk-3/GSK-3ß, daf-16/FOXO, bar-1/ß-catenin, daf-12/NR1H3, aak-2/AMPK and ptl-1/MAP, the biological targets that may be used by the compounds tested herein. The top 200 predictions are based on the score for association to seed genes as provided in Wormnet. Edge thickness is proportional to the global-evidence score as provided in Wormnet for each gene-to-gene interaction in the graph. Table S2 shows whether inactivating gene neighbors may suppress or enhance neuronal dysfunction in 128Q nematodes as indicated by the overlap between the 1267 predictions and 662 genes previously identified to modify neuronal dysfunction upon RNAi knock-down in these animals94. The graph was generated using Cytoscape 3.3.0. The Cytoscape’s layout used for the graph is of the force-directed and spring-embedded type. This network is enriched for signalling pathways, cellular components and biological processes that are relevant to stress response and neuronal activity (see Results).
