Fig. 3.
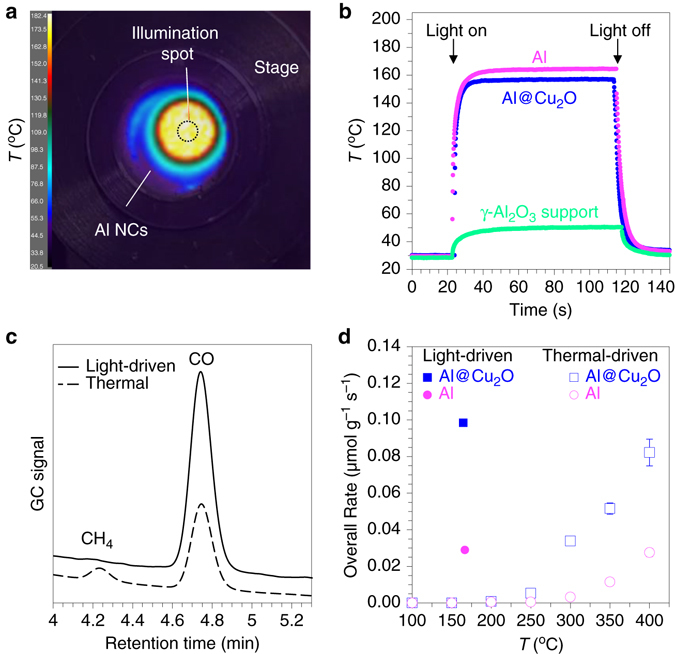
Light-driven vs. thermal-driven activity characterization for rWGS. a Spatial temperature mapping of the catalysts surface during illumination of Al NCs/γ-Al2O3 in air under visible light intensity of 10 W cm−2. b Steady-state temperature monitoring for oxide supported plasmonic nanoparticles compared to pure oxide support with and without irradiation in air. c Typical gas chromatogram of the chamber output during light (7 W cm−2) and thermal driven (350 °C) rWGS on Al@Cu2O. d The overall rate of products formation as a function of applied temperature in purely thermal-driven (light off) rWGS for oxide supported Al NCs and Al@Cu2O (unfilled data points). For comparison, the reaction rates during the light-induced process (10 W cm−2) are shown at the corresponding recorded temperatures for oxide supported Al NCs and Al@Cu2O (filled data points)
