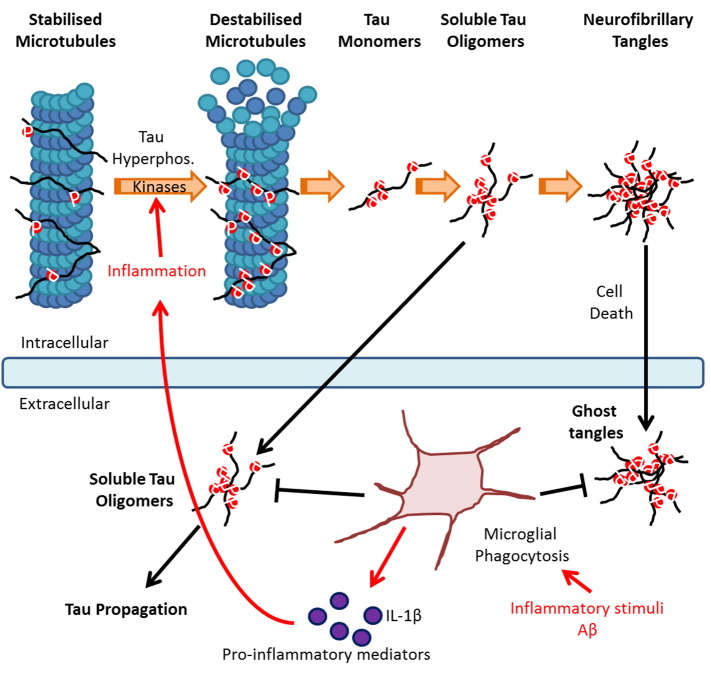
Fig. 1.
Progression of tau pathology: Under physiological conditions tau regulates microtubule stabilisation. In tauopathies, tau hyperphosphorylation triggers a loss in microtubule affinity. Soluble tau aggregates into pathological soluble tau oligomers, ultimately forming pathological insoluble neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). Tau oligomers are secreted into the extracellular compartment contributing to the propagation of tau pathology into neighbouring neurons. Inflammatory stimuli, such as Aβ, stimulate microglial production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β leading to the up-regulation of kinases involved in tau phosphorylation and exacerbation of the pathology. However, inflammation can have beneficial effects on tau pathology by inducing microglial phagocytosis of extracellular tau species. Image adapted from National Institute of Ageing.