FIG 1 .
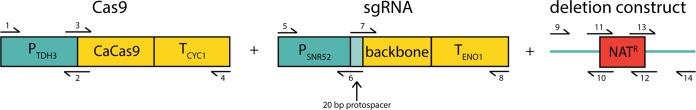
CRISPR components and targeting construct were optimized for transient CRISPR-Cas9 transformations in C. lusitaniae. Primers used to generate these constructs are shown, and their sequences are listed in Data Set S1 in the supplemental material. Cas9 was previously codon optimized for the Candida clade, CaCas9 (23), and the constitutive C. lusitaniae TDH3 promoter ensured maximal expression. The single guide RNA (sgRNA), which enables Cas9 to identify the target gene, was composed of the C. lusitaniae constitutive SNR52 promoter, a 20-bp protospacer sequence specific to the target gene, and the guide RNA backbone structure; terminator regions were included on both CRISPR components to help ensure efficient expression. Deletion constructs were also included in the transformation reaction to promote homology-directed repair of double-strand breaks created by Cas9. Two types of deletion constructs were generated by flanking a nourseothricin resistance marker (caSAT1) by either long (~1-kb) or short (~80-bp) regions of homology to the target gene. PCR construction of the long-flank deletion construct is shown in the figure; the short-flank deletion construct was generated using primers with ~80-bp homology to the target locus.