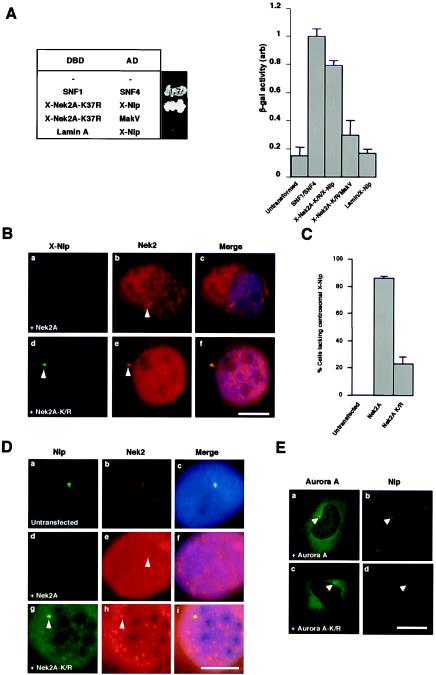
FIG.4.
Nek2A interacts with Nlp and displaces it from the centrosome. (A) Yeast two-hybrid interaction assay. The table on the left indicates the Gal4 DNA-binding domain (DBD) and activation domain (AD) fusion proteins expressed in S. cerevisiae with a photograph of the appropriate colonies after 5 days of growth on plates lacking histidine and adenine. The histogram on the right indicates β-galactosidase activity (arbitrary units) of the yeast strains as measured with an o-nitrophenylgalactopyranoside assay. Experiments were repeated three times, and error bars show the standard deviation. The activity of the positive control interaction between SNF1 and SNF4 was set at 1.0. (B) Xenopus A6 cells were transiently transfected with either human wild-type Myc-Nek2A (a to c) or the Myc-Nek2A-K/R kinase-inactive mutant (d to f) and, after 24 h, methanol fixed and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-Nek2 (R81, red) and anti-X-Nlp (R1679, green) antibodies. (C) The percentage of A6 cells in which the intensity of X-Nlp at the centrosome was significantly reduced or undetectable was calculated in untransfected cells and cells transfected with wild-type Nek2A or kinase-inactive Nek2A by counting >100 cells in three independent experiments. (D) Human U2OS cells were either untransfected (a to c) or transfected for 24 h with human Myc-Nek2A (d to f) or Myc-Nek2A-K/R (g to i) and stained with antibodies against human Nek2 (red) and Nlp (green). (E) Similarly, U2OS cells were transfected for 24 h with wild-type EGFP-Aurora A (a and b; green) or kinase-inactive EGFP-Aurora A-K162R (c and d; green) before processing with antibodies against endogenous Nlp (red). Scale bars in panels B, D, and E, 10 μm.