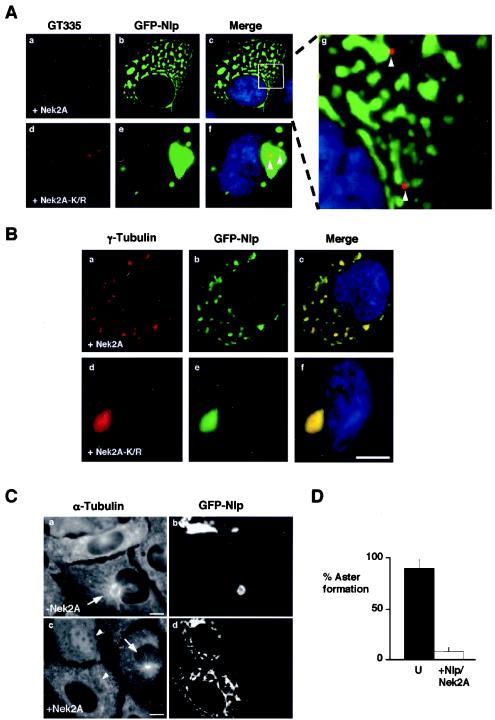
FIG. 8.
Nek2 does not prevent association of Nlp with γ-tubulin. (A) U2OS cells were cotransfected with GFP-Nlp and either wild-type Myc-Nek2A (a to c) or Myc-Nek2A-K/R (d to f) before methanol fixation after 24 h and processing for immunofluorescence microscopy. Centrioles stained with GT335 (red), GFP signals (green), and merged images including DNA stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue) are shown. Magnification of the inset box in panel c (g) highlights the fact that GFP-Nlp fragments do not colocalize with centrioles (arrows), whereas centrioles do colocalize with the large GFP-Nlp assembly when coexpressed with kinase-inactive Nek2 (arrows, panel f). (B) Cells processed as for panel A were stained with anti-γ-tubulin antibodies (red). GFP signals (green) and merged images including DNA stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue) are shown. (C) Microtubule regrowth assays were performed on cells transfected with GFP-Nlp alone (a and b) or GFP-Nlp plus Nek2A (c and d). Untransfected cells contain small radial microtubule asters emanating from the centrosome (c, arrow). Cells transfected with GFP-Nlp alone have large microtubule asters surrounding the single GFP-Nlp assembly (a, arrow). However, cells containing fragmented GFP-Nlp lack any such aster (c, arrowheads). (D) Histogram indicating the percentage of untransfected cells (U) with microtubule asters compared to cells cotransfected with GFP-Nlp and Nek2A. Scale bars, 10 μm.