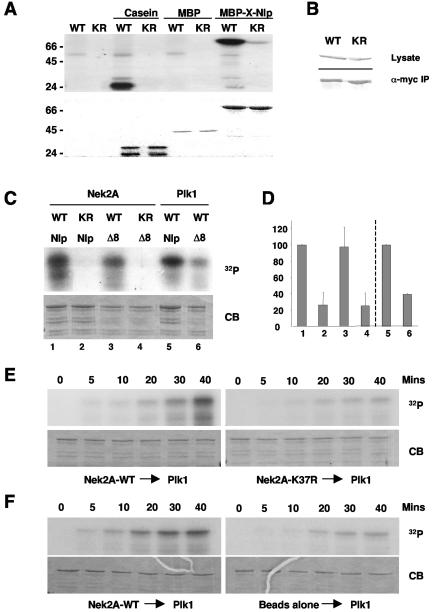
FIG. 9.
In vitro phosphorylation of Nlp by Nek2 and Plk1. (A) Purified MBP-X-Nlp262-552, MBP alone, and casein were phosphorylated in vitro by wild-type (WT) or kinase-inactive (KR) human Nek2A expressed in insect cells. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, stained with Coomassie blue (bottom panel), and exposed to autoradiography (top panel). (B) Western blots indicating equal expression (anti-Myc, top panel) and immunoprecipitation (anti-Nek2, bottom panel) of wild-type and kinase-inactive Myc-Nek2A proteins from transfected HeLa cells for use in kinase assays. (C) GST-Nlp-N-term (Nlp) or GST-Nlp-N-term-Δ8 (Δ8) was phosphorylated in vitro with Nek2A kinases immunoprecipitated from transfected HeLa cells or purified Plk1 expressed in insect cells, as indicated. (D) 32P incorporation into the Nlp proteins as shown in panel C was determined by scintillation counting. The level of phosphorylation of the GST-Nlp-N-term protein by wild-type Nek2 (1-4) and Plk1 (5, 6) was set as 100%. The histogram presents the average of three independent experiments. (E). GST-Nlp-N-term was incubated with either wild-type (left panels) or kinase-inactive (right panels) immunoprecipitated Nek2A for 40 min in the presence of unlabeled ATP. Purified Plk1 was then added together with [γ-32P]ATP and samples were taken at the times indicated before separation by SDS-PAGE. Gels were stained with Coomassie blue (CB) and exposed to autoradiography (32P). In each of five independent experiments, the phosphorylation of Nlp by Plk1 was always greater after incubation with wild-type compared to kinase-inactive Nek2A. (F) Kinase assays were performed as in panel E except that phosphorylation of Nlp by Plk1 was assayed after incubation with either immunoprecipitated Nek2A (left panels) or protein G-Sepharose beads alone (right panels).