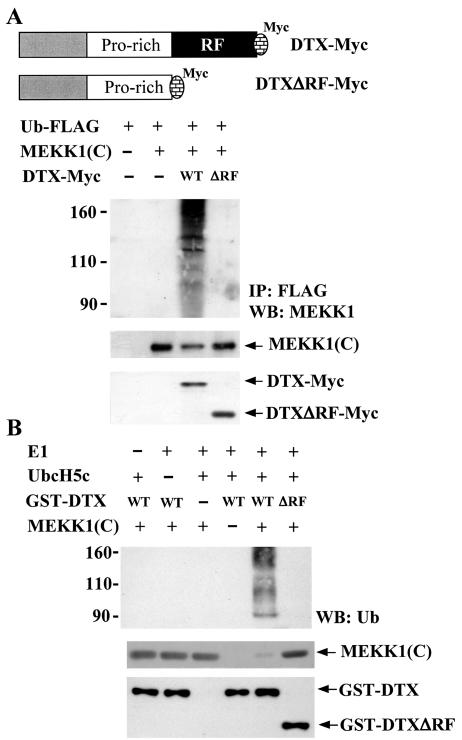
FIG. 9.
Ubiquitination of MEKK1(C) by Deltex but not DeltexΔRF in vivo and in vitro. (A) 293T cells were transfected with Ub-FLAG, MEKK1(C), DTX-Myc, or DTXΔRF-Myc as indicated. Schematic representations of DTX-Myc and DTXΔRF-Myc are shown. Forty-eight hours after transfection, 293T cells were treated with MG132 (25 μM) for 5 h and total cellular extracts were prepared. Ubiquitinated proteins were immunoprecipitated from 200 μg of total cellular extracts by FLAG-M2 affinity gel. The precipitates were resolved on SDS-PAGE and the presence of MEKK1(C) [representing ubiquitinated MEKK1(C)] determined using anti-MEKK1 (upper panel). Protein levels of MEKK1(C), DTX, or DTXΔRF in the cell extracts were detected using anti-MEKK1 or anti-Myc (lower panels). (B) In vitro ubiquitination assays were performed in reaction mixtures containing bovine ubiquitin, E1, E2 (UbcH5c), His-MEKK1(C), GST-DTX, or GST-DTXΔRF fusion protein as indicated. Reactions were incubated at 30°C for 30 min. His-MEKK1(C) was then captured by Ni-NTA agarose, separated on a SDS-8% PAGE, and blotted with ubiquitin antibody (upper panel). Ubiquitination of MEKK1(C) led to the appearance of multiple forms of higher-molecular-weight MEKK1(C). The input of GST-DTX (including GST-DTXΔRF) and His-MEKK1(C) fusion proteins in the reaction mixture is shown in the bottom panel.