FIG. 1.
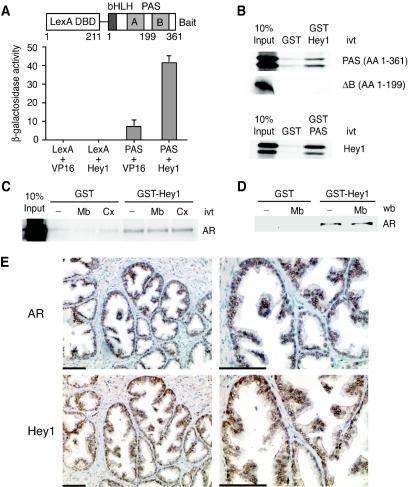
Hey1 interacts with SRC1 and AR. (A) The L40a yeast strain expressing either LexA-DBD (LexA) or LexA-DBD fused to the SRC1 bHLH-PAS domain (PAS) was transformed with either an empty pASV3 plasmid (VP16) or pASV3 expressing Hey1 fused to the VP16 activation domain (Hey1). β-Galactosidase activity in each yeast extract was measured in duplicate. Data represent the means + SD of results with two independent transformants. The schematic representation of the LexA chimera used as bait in the yeast two-hybrid screening is shown above. (B) Hey1 interacts in vitro with the SRC1 bHLH-PAS domain. GST fusion proteins coupled with Sepharose beads were incubated with in vitro-translated (ivt) [35S]methionine-labeled Hey1 or SRC1 fragments as indicated. After being washed extensively, samples were boiled and separated by SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Gels were fixed and dried, and the labeled proteins were detected by fluorography. AA, amino acids. (C) Hey1 interacts in vitro with AR. GST alone or GST-Hey1 were incubated with 35S-labeled AR, in the presence of vehicle (−), 100 nM mibolerone (Mb), or 10 μM Casodex (Cx). (D) Whole-cell extracts from LNCaP cells were incubated with GST alone or GST-Hey1 bound to glutathione-Sepharose in the presence of vehicle (−) or 100 nM Mb. The associated AR was detected by immunoblotting using anti-AR antibody. wb, Western blot. (E) AR and Hey1 colocalize in prostate epithelial cells. Adjacent sections of human BPH samples were stained with anti-AR antibodies (top panels) or anti-Hey1 antibodies (bottom panels). Two different magnifications are shown (scale bar = 100 μm). The brown color reflects positive staining for AR or Hey1, and negative nuclei are blue.