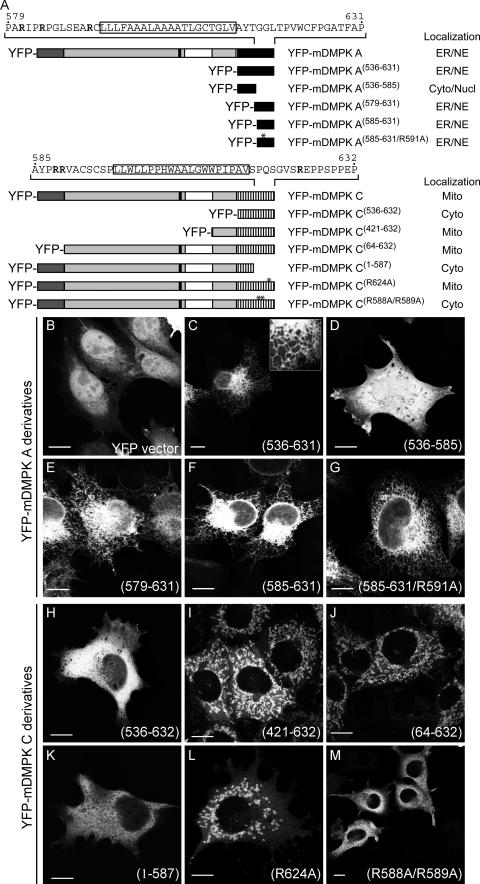
FIG.6.
Involvement of basic residues in tail anchors in localization of mDMPK A and C. (A) Schematic representation of mDMPK A and C deletion constructs and their subcellular localization: ER, NE (nuclear envelope), Cyto (cytosol), Nucl (nucleus), Mito (mitochondrial). (B to M) Confocal images of fluorescent YFP-tagged DMPK A or C deletion mutants in N2A cells. Transfected N2A cells expressing unmodified YFP were used as the control (B). ER localization of mDMPK A deletion constructs was found for tail 1 alone (YFP-mDMPK A(536-631)) (C) and YFP-mDMPK A(579-631) (E), YFP-mDMPK A(585-631) (F), and YFP-mDMPK A(585-631/R591A) (G), but not for YFP-mDMPK A(536-585) (D). Tail 2 of mDMPK C alone did not target to mitochondria (YFP-mDMPK C(536-632)) (H), whereas YFP-mDMPK C(421-632) (I) and YFP-mDMPK C(64-632) (J) yielded a mitochondrial localization. The C-terminal 45 amino acids are essential for mitochondrial localization (YFP-mDMPK C(1-587) (K) and also the basic residues therein, since expression of YFP-mDMPK C(R624A) results in rounded and fragmented mitochondria (L) whereas YFP-mDMPK C(R588A/R589A) localizes to the cytosol (M). Bars, 10 μm.