Figure 5. Aap processing by S. epidermidis secreted proteases.
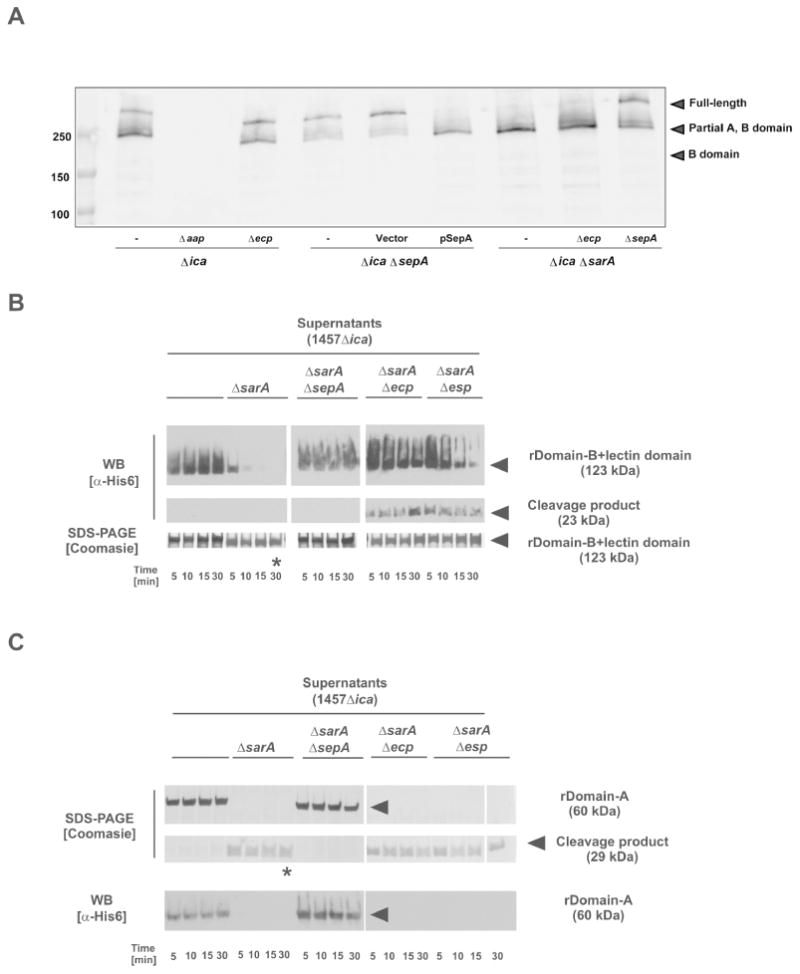
A. Western blot of cell wall preparations from S. epidermidis 1457Δica background strains. Samples were blotted and analyzed using a rabbit anti-rDomain B antiserum. Bound antibodies were detected using anti-rabbit IgG coupled to IR800 (Licor). B. Analysis of rDomain-B_LLD cleavage by incubation with concentrated cell-free supernatants protease overexpressing strain 1457ΔicaΔsarA and corresponding protease knock-out mutants incubated with rDomain-B_LLD. After incubation at 37 °C reactions were loaded onto 4-15 % gradient gels. After separation proteins were stained using Coomassie blue or blotted onto PVDF membrane. Proteins were detected using a mouse anti-His6 IgG and an anti-mouse IgG coupled to peroxidase. * indicates band for which the N-terminal sequence was determined. C. Analysis of rDomain-A cleavage by incubation with concentrated cell-free supernatants protease overexpressing strain 1457ΔicaΔsarA and corresponding protease knock-out mutants incubated with rDomain-B+212. After incubation at 37 °C reactions were loaded onto 4-15 % gradient gels. After separation proteins were stained using Coomassie blue or blotted onto PVDF membrane. Proteins were detected using a mouse anti-His6 IgG and an anti-mouse IgG coupled to peroxidase. Results shown in panel B and C were obtained using supernatants from S. epidermidis 1457-M10ΔsarA and corresponding protease knock-out mutants.
