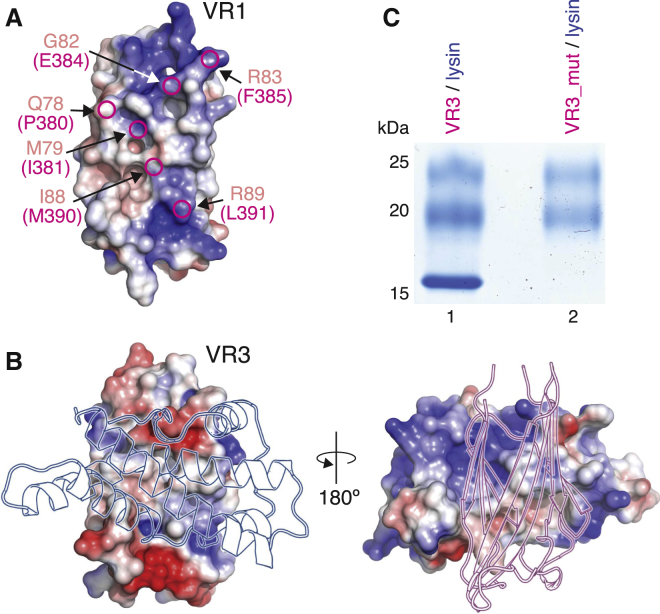
Figure 5.
Substitution of VR3 Interface Residues Explains Why VR1 Does Not Bind Lysin
(A) VR1 surface colored by electrostatic potential. Circles mark non-positively selected amino acids of VR1 (salmon) that differ from VR3 residues (magenta) at the interface with lysin.
(B) Unlike the corresponding region in VR1 (A), the interacting surface of VR3 (left) is electrostatically complementary to that of lysin (right).
(C) A VR3 mutant where the residues highlighted in (A) are replaced by the corresponding residues of VR1 (VR3_mut, lane 2) does not pull down lysin.