Abstract
In situ hybridization and RNA blot-hybridization techniques were used (i) to examine the regional distribution of mRNA for a putative kainate receptor in adult rat brain and ii) to test the possibility that seizures affect expression of the receptor gene. The highest densities of hybridization were distributed within hippocampal pyramidal and granule cells, medial habenula, Purkinje cells and the molecular layer of cerebellum, and olfactory bulb. Recurrent limbic seizures caused a massive, delayed, and reversible reduction in levels of the kainate receptor mRNA in dentate gyrus; lesser decreases were found in pyramidal cell fields of hippocampus and superficial cortex. These findings provide evidence that unusual patterns of physiological activity can alter genomic expression for a subclass of glutamate receptors in brain.
Full text
PDF
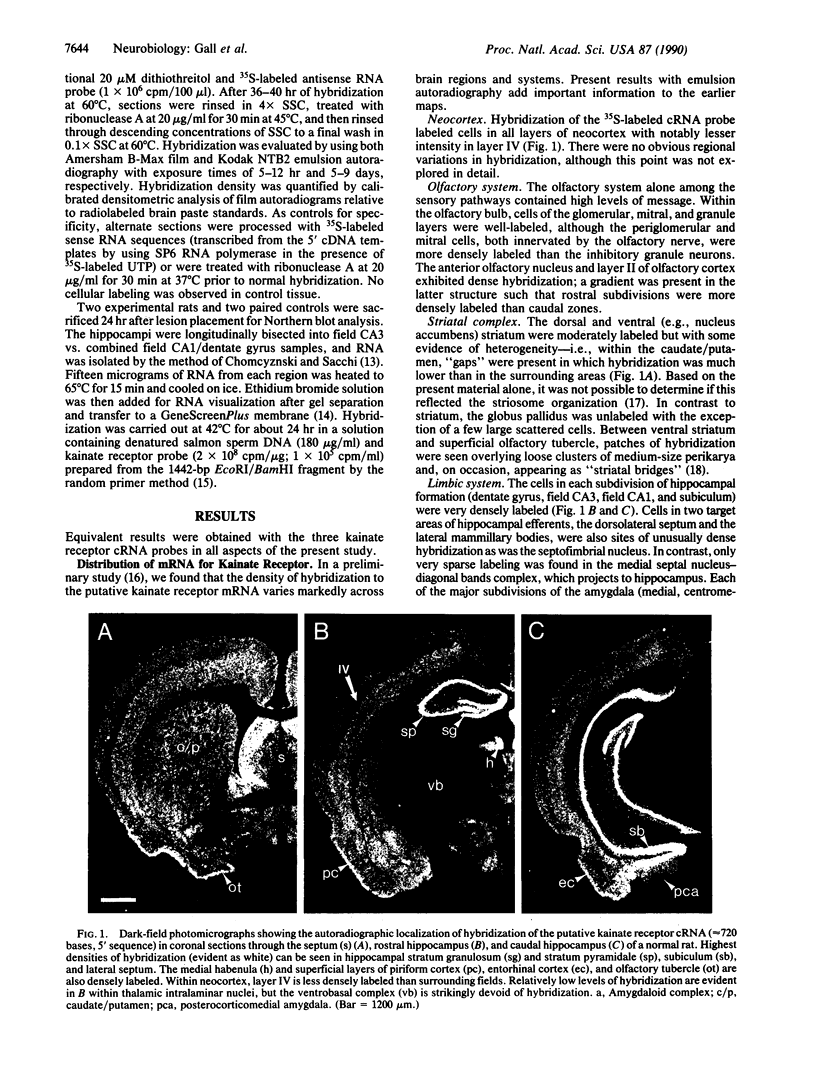

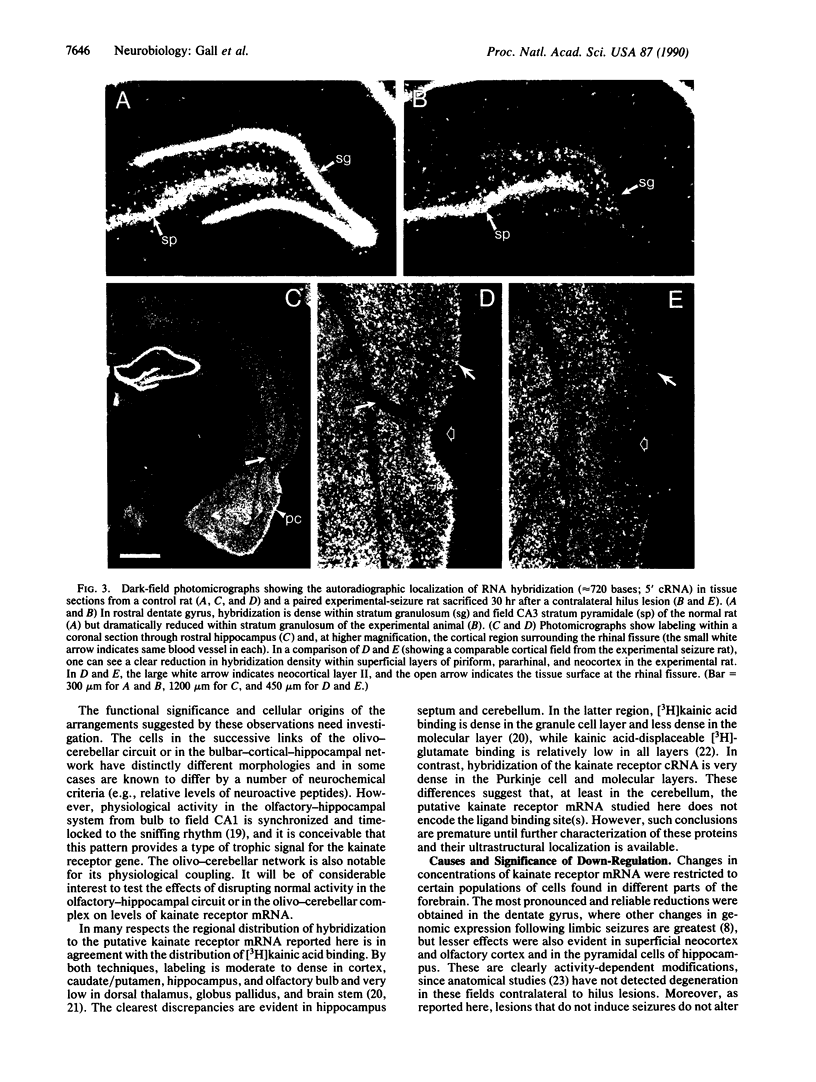

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brehm P., Henderson L. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor channel function during development of skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. A., Bank B., Milgram N. W. Epileptogenic effects of electrolytic lesions in the hippocampus: role of iron deposition. Exp Neurol. 1984 Dec;86(3):506–514. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(84)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Isackson P. J. Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. Seizures induce dramatic and distinctly different changes in enkephalin, dynorphin, and CCK immunoreactivities in mouse hippocampal mossy fibers. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):1852–1862. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-01852.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Histochemically distinct compartments in the striatum of human, monkeys, and cat demonstrated by acetylthiocholinesterase staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5723–5726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer L., Zaborszky L., Zahm D. S., Alheid G. F. The ventral striatopallidothalamic projection: I. The striatopallidal link originating in the striatal parts of the olfactory tubercle. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 22;255(4):571–591. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrides F., Eichenbaum H. B., Forbes W. B. Temporal relationship between sniffing and the limbic theta rhythm during odor discrimination reversal learning. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1705–1717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01705.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. The distribution of [3H]kainic acid binding sites in rat CNS as determined by autoradiography. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 2;252(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90981-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Yao D., Cotman C. W. L-[3H]Glutamate binds to kainate-, NMDA- and AMPA-sensitive binding sites: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 12;340(2):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90936-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pico R. M., Gall C. Continuities between outer nuclear membrane and the rough endoplasmic reticulum increase in hippocampal neurons during seizure-induced protein synthesis. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 18;497(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racine R. J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Mar;32(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffen D. W., Cole A. J., Worley P. F., Christy B. A., Ryder K., Baraban J. M. Convulsant-induced increase in transcription factor messenger RNAs in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7795–7799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Miledi R. Repression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression by antisense RNAs and an oligonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1302–1306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Wamsley J. K. Autoradiographic localization of high-affinity [3H]kainic acid binding sites in the rat forebrain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. D., Gall C. M. Differential regulation of neuropeptide and proto-oncogene mRNA content in the hippocampus following recurrent seizures. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. D., Gall C. M., McKelvy J. F. Enkephalin biosynthesis and enkephalin gene expression are increased in hippocampal mossy fibers following a unilateral lesion of the hilus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):753–759. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00753.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








