Figure 2. Enzyme zones and their effects on multi-step, continuous-flow biocatalysis.
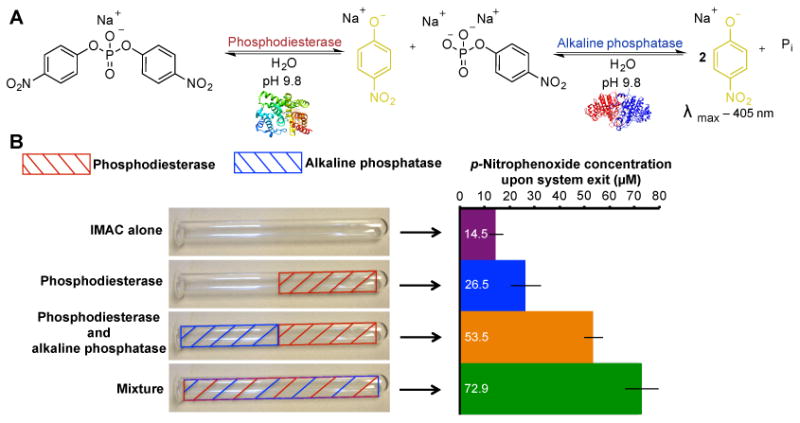
A) A two-step biosynthetic pathway was used to examine enzyme zones in multistep activity. Here, phosphodiesterase transforms the bis(p-nitrophenol)phosphate monosodium salt into p-nitrophenoxide (absorbance at 405 nm) and p-nitrophenol phosphate. The next enzyme in the pathway, alkaline phosphatase, transforms the p-nitrophenol phosphate to another molecule of p-nitrophenoxide and inorganic phosphate (Pi). Monitoring the concentration of p-nitrophenoxide liberated by the reaction determines the pathway efficiency. B) In this experiment, the reactor is divided into distinct zones, with each zone containing either phosphodiesterase (red) or alkaline phosphatase (blue). Each reactor is then tested under continuous flow conditions (0.5 mL min−1) for the quantification of p-nitrophenoxide concentration. Using a mixture of enzymes yielded 72.9 μM product (4% conversion efficiency in ≈10 min). Error is indicated as standard deviation around the mean (n=10 independent replicates).
