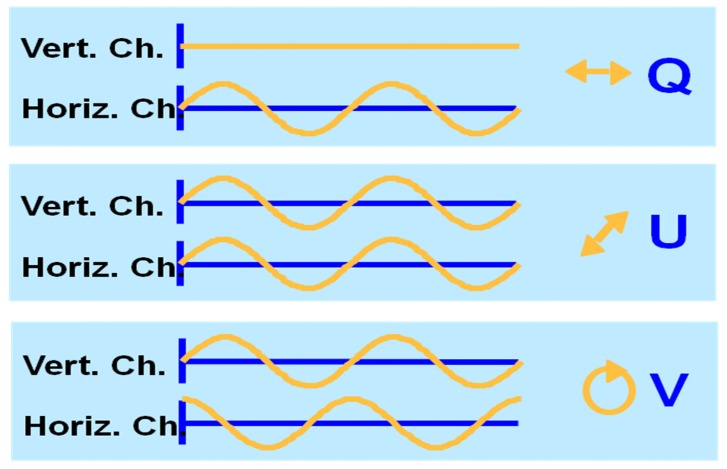
Fig. 8.
Example of the interference fringes measured in the horizontal and vertically polarized channel. If the amplitude in the vertical channel is zero, the light must be horizontally polarized (Q-state in Stokes vector notation). If the interference fringes are of equal magnitude and are in phase, the polarization state is linear at 45 degrees (U-state in Stokes vector notation). If the interference fringes are of equal magnitude and are 90 degrees out of phase, the polarization state is circular (V-state in Stokes vector notation) .