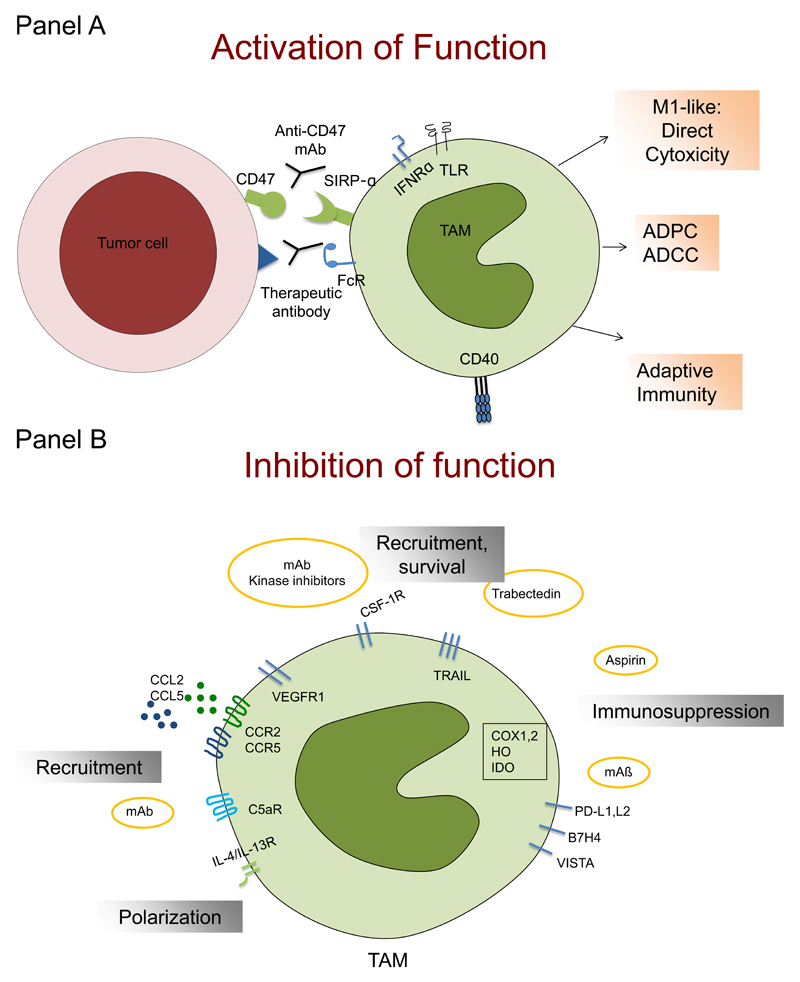
Figure 3. Schematic representation of strategies targeting macrophages in tumor settings.
Macrophage-centered therapeutic approaches are aimed either at activating their antitumor activity (Panel A) or inhibiting their recruitment and functions related to tumor promotion (panel B).
Panel A: the concerted action of microbial moieties (acting via TLRs) and IFNγ induces M1-like functional polarization and can activate macrophage killing of tumor cells; macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) can mediate the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies; interference with the SIRPα-CD47 pathway activates macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent phagocytosis (ADCP) and results in functional skewing of macrophages in an M1 direction and antitumor activity; an anti-CD40 antibody re-educates M2-like macrophages in the tumor microenvironment, leading to re-establishment of tumor immune surveillance.
Panel B: Inhibition of monocyte-attracting molecules, including chemokines (e.g CCL2, CCL5), VEGF, CSF-1 and complement mediators (C5a) with specific monoclonal antibodies (e.g. carlumab, emactuzumab) or antagonists (e.g. maraviroc) prevent macrophage recruitment to the tumor microenvironment, reducing tumor growth and dissemination; inhibitors of CSF-1 have also the potential to inhibit macrophage survival; Trabectedin activates a caspase-dependent pathway of apoptosis, selectively in cells of the monocyte lineage, causing a partial depletion of circulating monocytes and TAM; the protective function of NAIDS, aspirin in particular, against primary cancer and metastasis relies on the inhibition of prostaglandin production, which have immunosuppressive properties; TAM contribute to suppression of adaptive immunity by expression of immunosuppressive molecules, such as IDO, cyclooxygenases (COX1,2), TGFβ and IL-10. Moreover, TAM express triggers of checkpoint blockade, such PD-L1, PD-L2, B7H4 and VISTA.
TLR: Toll-like receptors; IFNRα: interferon receptor alpha; FcR: Fc receptor, mAb: monoclonal antibody; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; CSF-1: colony-stimulating factor; NAIDS: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; IDO: indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase; TGFβ: transforming growth factor β; IL-10: interleukin 10.