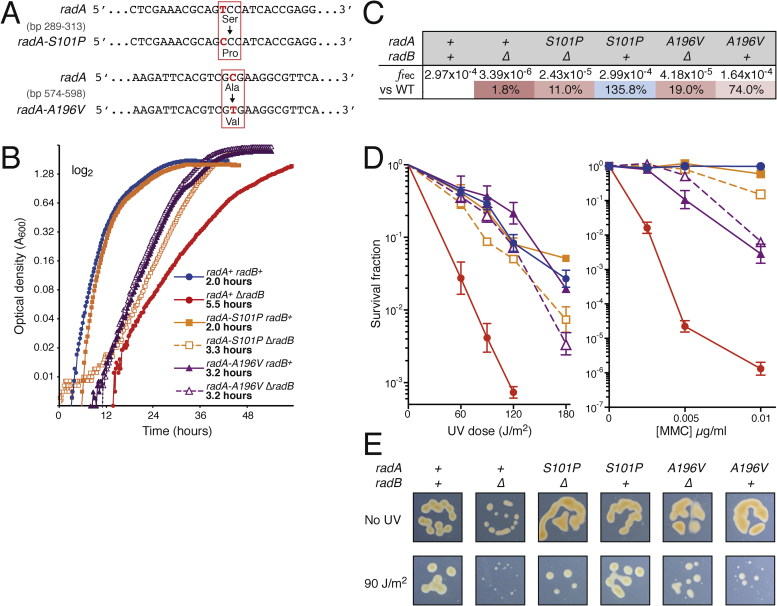
Fig. 3.
(A) Base substitutions in radA that result in radA-S101P and radA-A196V. (B) ΔradB strains have a growth defect in broth compared to wild-type, and radA-S101P (H1428) or radA-A196V (H724) suppress this defect. Data was plotted as in Fig. 2B. (C) Both radA-S101P and radA-A196V alleviate the recombination defect of ΔradB strains. Recombination frequency (frec) was measured using the assay shown in Supplemental Fig. S1. Transformants per μg DNA per cell was calculated as an average of ≥3 independent repeats; percentages indicate recombination frequency compared to wild-type. D) Both radA-S101P and radA-A196V suppress the DNA damage defect of ΔradB. Survival following DNA damage (UV, left. MMC, right) is calculated relative to an unirradiated control, see panel B for key. Each data point is an average of ≥3 independent repeats; standard error is shown. E) Strains expressing radA-A196V recover more slowly than strains expressing radA-S101P after UV-irradiation. Cultures were spotted onto complete media and treated with 90 J/m2 of UV (or no UV as a control); colony size was observed after 5 days. All spots are 10−5 dilution except for the irradiated ΔradB, which is 10−2.