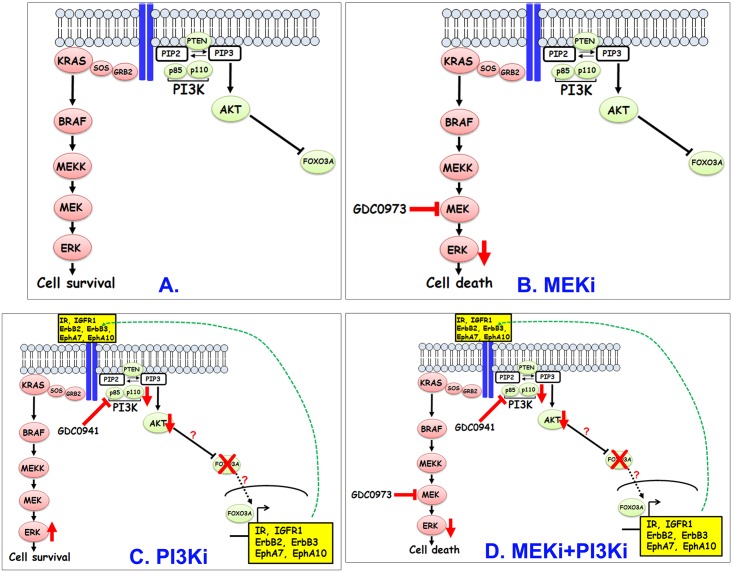
Fig 6. A model to explain the enhanced effectiveness of MEKi and PI3Ki in reducing viability of KRAS-mutant MCA cells.
MEKi treatment (B) reduces pERK levels and leads to increased cell death. In contrast, PI3K inhibition (C) initially reduces AKT signaling but this reduction leads to enhanced expression of RTKs including IR, IGFR1, EphA10, EphA7, ErbB2 and ErbB3 presumably through relief of inhibition of FOXO proteins. Increased expression of these RTKs leads to their increased activation (likely through receptor homo- or heterodimerization) which in turn, stimulates rebound activation of MEK-ERK pathway which in turn, enhances survival and development of resistance. Combined inhibition of PI3K and MEK (D) prevents rebound activation of ERK in response to PI3K single agent treatment and helps overcomes resistance.