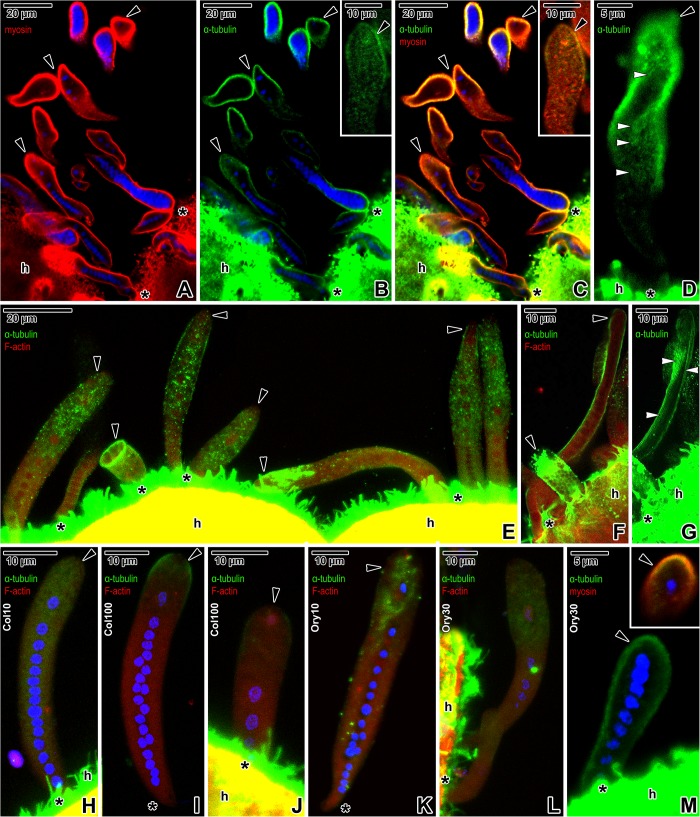
Fig 7. Distribution of myosin (TRITC), α-tubulin (FITC) and F-actin (TRITC) in Siedleckia nematoides before and after application of cytoskeletal drugs.
A–G. Non-treated parasites. A-B. Single optical section revealing the localisation of myosin (A) and α-tubulin (B). The inset in B shows a localisation of α-tubulin in a caudal part of an individual from another optical section. C. Composite view showing the co-localisation of myosin and α-tubulin in a single optical section of parasites shown in A-B. The inset shows a co-localisation of myosin and α-tubulin in a caudal part of an individual from another optical section. D. The localisation of α-tubulin in the superficial region of a gamont. E. Co-localisation of α-tubulin and F-actin in parasites of various developmental stages. F. Composite view revealing the co-localisation of α-tubulin and F-actin in a macrogamont and microgamont in a single optical section. G. More superficial optical section revealing the localisation of α-tubulin in macrogamont shown in F. H-J. Co-localisation of α-tubulin and F-actin in parasites treated with colchicine: H. 10 mM colchicine (2 h). I-J. 100 mM colchicine (1 h). K-M. Co-localisation of α-tubulin and F-actin in parasites treated with oryzalin: K. 10 μM oryzalin (8 h). L. 30 μM oryzalin (7 h). M. Labelling of α-tubulin in a trophozoite treated with 30 μM oryzalin (5 h). The inset shows a co-localisation of α-tubulin and myosin in the trophozoite caudal region. Note the patchy distribution of α-tubulin underlying the pellicle, corresponding to the localisation of subpellicular microtubules. A-C, M: CLSM, IFA/Hoechst, methanol fixation; D: CLSM, IFA, methanol fixation; E-F: CLSM, IFA/phalloidin-TRITC, PFA fixation; G: CLSM, IFA, PFA fixation; H-L: CLSM, IFA/phalloidin-TRITC/Hoechst, PFA fixation. black arrowhead–parasite caudal end, black asterisk–parasite apical end, h–host tissue, white arrowheads–tiny longitudinal lines corresponding to the subpellicular microtubules.