Fig. 3.
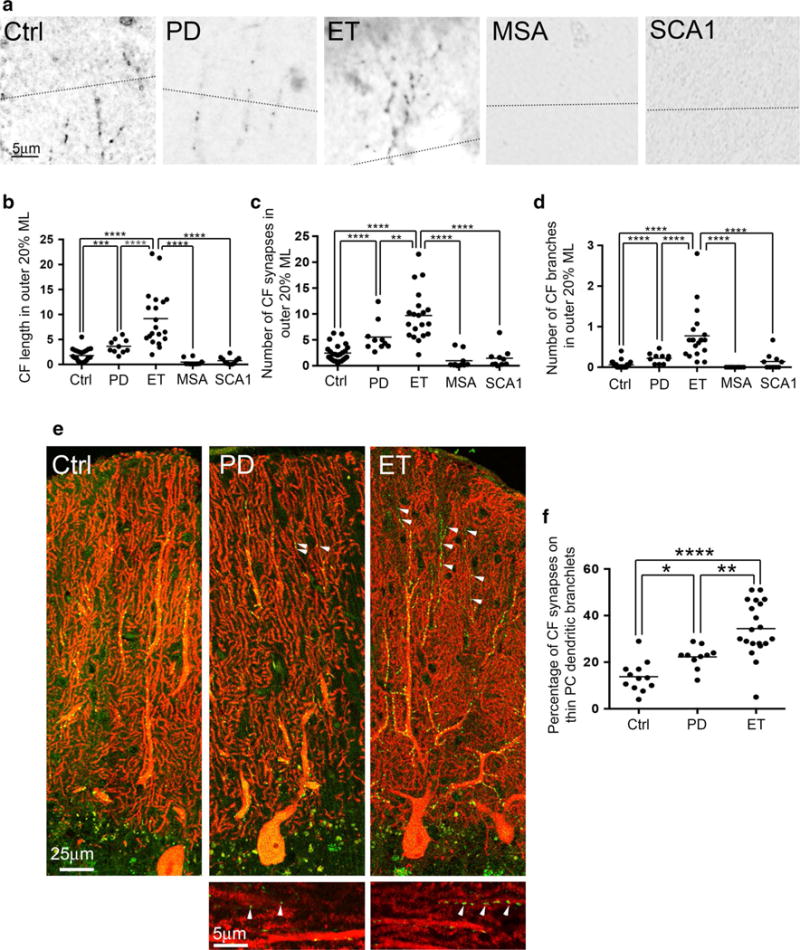
CF morphology in the outer 20 % of the molecular layer and CF synapses on the thin PC dendritic branchlets. The dotted line indicates the border between the outer 20 % and inner 80 % of the molecular layer (a). Representative cerebellar sections labeled with anti-VGlut2 antibody of a control, a PD case, an ET case, an MSA case, and an SCA1 case demonstrate more complex CF synaptic pathology in the ET case (a). In ET cases, there are increased CF length (b), increased CF synapses (c), and increased number of CF branches (d) in the outer 20 % of the molecular layer when compared to other diagnostic groups. Representative images of dual immunofluorescence with anti-VGlut2 (Alexa 488, green) and anti-calbindinD28k antibody (Alexa 594, red) of cerebellar sections of a control, an ET case and a PD case (e) and CF synapses on the thin PC dendritic branchlet <1 μm in diameter are shown (arrowheads in e). ET cases have increased percentage of CF synapses on the thin PC dendritic branchlets <1 μm in diameter when compared to PD cases and controls (f), and this feature is also increased, but to a lesser extent, in PD compared to controls. Ctrl control, PD Parkinson’s disease, ET essential tremor, MSA multiple system atrophy, SCA1 spinocerebellar ataxia type 1, CF climbing fiber. ML molecular layer, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ****p < 0.001
