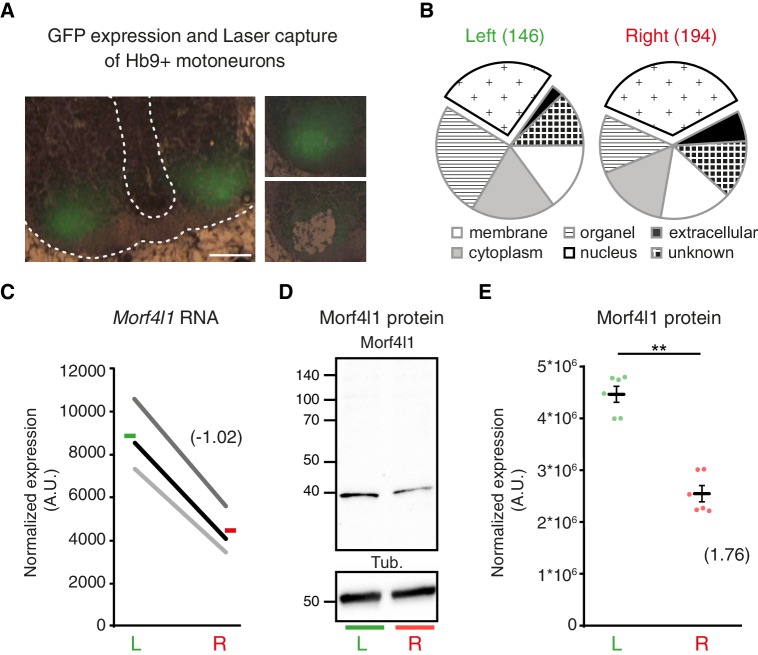
Figure 4. L/R molecular signature of cervical motoneurons.
(A) Transverse sections of E11.5 Hb9::GFP embryo cervical spinal cord, illustrating the areas used for laser-capture microdissection. (B) Pie charts showing the proportion of left-enriched and right-enriched genes according to their Gene Ontology ‘cellular component’ terms. The ‘nucleus’ component is detached from the pie. (C) Ladder graph showing the left and right expression of Morf4l1 in three embryos. Average L/R fold-change shown in brackets. (D) Immunodetection of Morf4l1 and loading control tubulin (Tub.) in left and right ventral cervical spinal cord tissues. (E) Graph showing normalized protein levels of Morf4l1 in left and right ventral cervical spinal cords from E11.5 mouse embryos. Individual values observed for the six western-blots (dots) and mean ± SEM are represented (L/R ratio: 1.81 ± 0.163, L versus R; p=0.0022, Wilcoxon signed rank). Average L/R fold-change shown in brackets. Scale bar: 100 μm. Numerical values used to generate the graphs are accessible in Figure 4—source data 3.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18481.016