Figure 3.
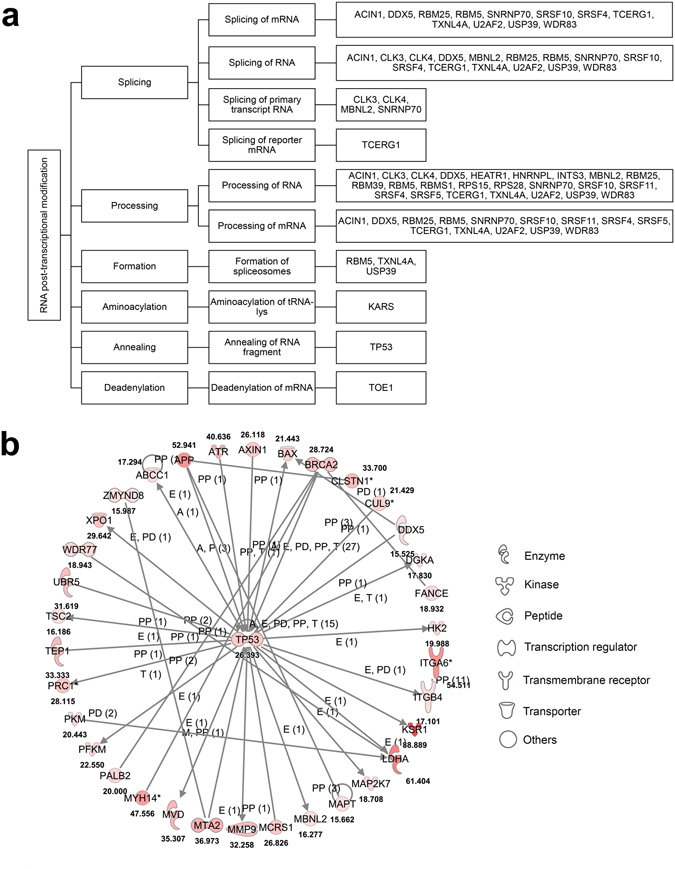
Hypoxia-regulated intron retention targets are involved in RNA post-transcriptional modification and cancer function. (a) Tree diagram showing functional distribution of chronic hypoxia-regulated genes with significantly upregulated intron retention events (FDR < 0.01 and |ΔSI| ≥ 15%) that are involved in RNA post-transcriptional modification processes. (b) Network of hypoxia-regulated genes with significantly up-regulated intron retention events involved in cancer function. The network was generated using IPA with the criteria that only experimentally observed, direct relationships in human were used. Numbers indicate the ΔSI for each gene. The types of relationships include expression (E), protein-protein interactions (PP), activation (A), transcription (T), protein-DNA interactions (PD) and modifications (M).
