Figure 3.
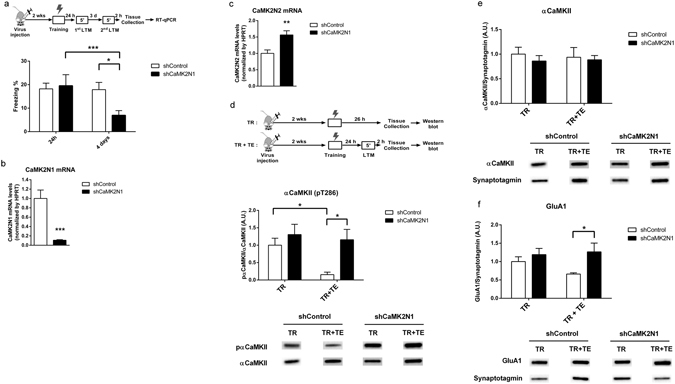
CaMK2N1 expression is necessary for contextual fear LTM maintenance after retrieval and regulates synaptic CaMKII T286 autophosphorylation and GluA1 levels. (a) Dorsal hippocampi of mice were transfected with rAAV expressing either control shRNA (n = 15) or CaMK2N1 shRNA (n = 11). Contextual fear LTM was determined one day after conditioning and for a second time 4 days after conditioning. CaMK2N1 shRNA expression in hippocampus impaired contextual fear LTM after retrieval. (b) All mice in (a) had a significant knockdown of CaMK2N1 mRNA expression in hippocampus. (c) In this cohort of mice, knockdown of CaMK2N1 caused a significant increase in CaMK2N2 mRNA expression. (d) To understand the retrieval-induced effects of CaMK2N1 knockdown mice were treated with shCaMK2N1 rAAV treatment and trained and tested (TR + TE) in the CFC paradigm or just trained (TR). Dorsal hippocampi samples were collected 2 hours after retrieval of contextual fear LTM, and protein samples prepared for western blots. Retrieval of contextual fear LTM significantly decreased αCaMKII autophosphorylation at T286 in synaptosomes (shControl: TR, n = 7, TR + TE, n = 5). This decrease in T286 autophosphorylation was impaired by shCaMK2N1 expression (TR, n = 7; TR + TE, n = 7). (e) shCaMK2N1 expression did not impact on αCaMKII protein levels (shControl: TR, n = 7, TR + TE, n = 6; shCaMK2N1: TR, n = 7; TR + TE, n = 7) (see statistics on Supplementary Table S4). (f) Quantification of GluA1 synaptosomal levels of the same cohort of animals revealed a retrieval-dependent increase due to CaMK2N1 knockdown (shControl: TR, n = 6, TR + TE, n = 5; shCaMK2N1: TR, n = 7; TR + TE, n = 7). Example immunoblotting staining for these proteins can be found below each graph and in Supplementary Fig. S7. Mean and S.E.M.; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
