Figure 3.
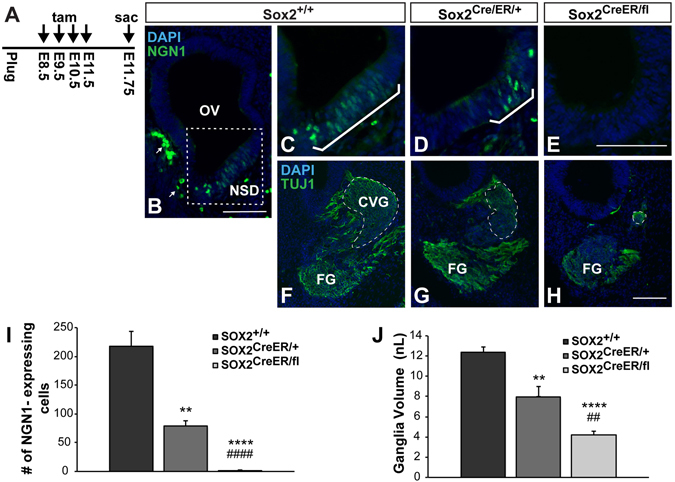
SOX2 dose-dependently regulates inner ear neurogenesis. (A) Chronic tamoxifen injection paradigm used for deleting Sox2 throughout inner ear neurogenesis. (B) Low magnification view of the Sox2 +/+ control otic vesicle, showing the location of the neurosensory domain (dotted box). Arrows point to non-specific staining of blood cells outside the epithelium, which could be easily distinguished from NEUROG1-positive cells based on their cellular shape. (C–E) Representative sections showing that the number of NEUROG1-expressing neuroblasts (brackets) is reduced according to the Sox2 gene dosage. (E) The total number of NEUROG1-positive cells was quantified and found to be significantly decreased in both Sox2 CreER/+ mice (***p = 0.0003) (n = 7) and Sox2 CreER/fl mice (****p < 0.0001) (n = 7) compared to Sox2 +/+ controls (n = 6), and between Sox2 CreER/+ and Sox2 CreER/fl mice (#### p < 0.0001) (one-way ANOVA followed by Student’s t test with a Bonferroni correction). (E-H) Representative sections showing that the CVG (outlined with dashed lines) is similarly reduced according to Sox2 genotype. (I) The total volume of the CVG was quantified from serial sections and found to be significantly decreased in both Sox2 CreER/+ mice (**p = 0.003) and Sox2 CreER/fl mice (****p < 0.0001) compared to Sox2 +/+ controls, and between Sox2 CreER/+ and Sox2 CreER/fl mice ( ## p = 0.004) (one-way ANOVA followed by a Student’s t test with a Bonferroni correction). Error bars represent SEM. OV: Otic vesicle; NSD: Neurosensory domain; CVG: Cochleovestibular ganglion; FG: Facial ganglion. Scale bars: 100 μm.
