Figure 5. MCM8 enhanced CDK4 kinase activity.
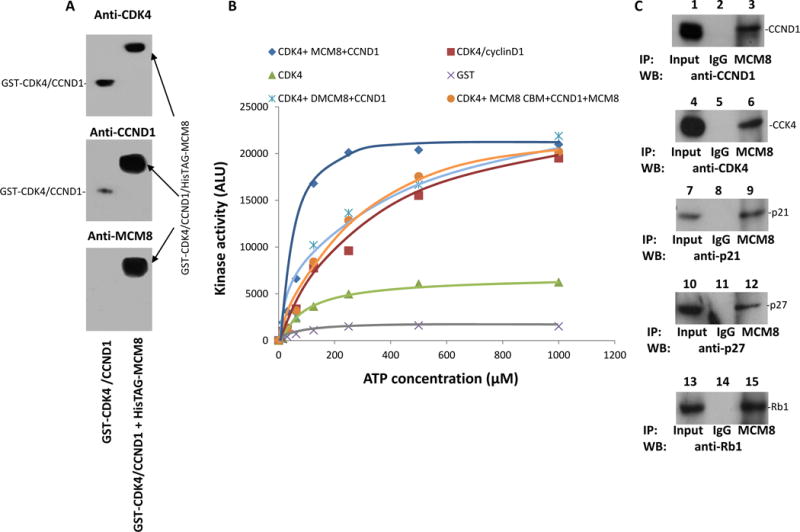
(A) Complex formation of GST-CDK4/cyclin D1/HisTAG-MCM8. The binding assays were performed on E.coli produced GST-CDK4 with GST-CCND1 (lane 1) or GST-CDK4 with GST-CCND1 and HisTAG-MCM8 (lane 2). The GST-CDK4/cyclin D1/HisTAG-MCM8 complex was purified from HisTAG column, resolved in 6% non-denaturing gel, and immunoblotted with antibodies specific for CDK4, cyclin D1 or MCM8. (B) One hundred nanograms of GST-CDK4/CCND1 (from Sf9 cells) were incubated with various concentrations of ATP as indicated and 50 ng of Rb, in the absence or presence of MCM8 or ΔMCM8delaa261-290 (dMCM8) or ΔMCM8aa261-290 (MCM8 cyclin D1 binding motif –MCM8 CBM) plus MCM8 for 30 min at 37°C using ATP-GLO™ kinase assay kit. CDK4 and GST were used as controls. Rb phosphorylation quantified after immunoprecipitation using antibodies specific for Rb protein. (C) MCM8 co-immunoprecipitated with p27, p21, cyclin D1 and CDK4 in PC3 cells.
