Figure 5.
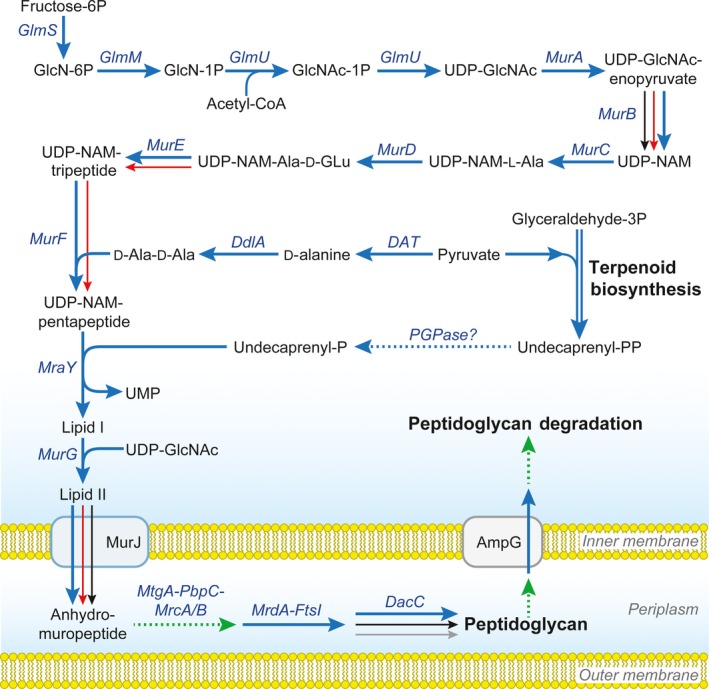
Genes involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis in selected members of the family Anaplasmataceae.
Biosynthesis pathways of peptidoglycan for N. helminthoeca, N. risticii, N. sennetsu, E. chaffeensis, E. ruminantium, A. phagocytophilum, A. marginale and Wolbachia wMel endosymbiont of Drosophila melanogaster were downloaded from KEGG database (http://www.genome.jp) and analysed. N. helminthoeca, A. marginale and Wolbachia wMel encode nearly all genes for peptidoglycan biosynthesis pathways (blue arrows), except that A. marginale and Wolbachia wMel lacks genes for the biosynthesis of d‐Ala‐d‐Ala. In addition, all members in the family Anaplasmataceae encode terpenoid biosynthesis pathways like isopentenyl‐, farnesyl‐ and geranyl‐diphosphate; however, only Neorickettsia and Wolbachia spp. encode undecaprenyl diphosphate (Und‐PP) synthase (UppS) to produce Und‐PP. N. helminthoeca encodes two PGPases (NHE_RS00895 and NHE_RS01205) that might produce Und‐P from Und‐PP. Genes present in N. risticii and N. sennetsu, red arrows; A. phagocytophilum, black arrows; E. chaffeensis and E. ruminantium, grey arrow. Dashed green lines, genes absent in all bacteria analysed; dashed blue line, potential pathway present. Diagram was modified from KEGG pathways and Gillespie et al. (2010). Abbreviations: GlcN, d‐Glucosamine; GlcNAc, N‐Acetyl‐α‐d‐glucosamine; UDP‐NAM, UDP‐N‐acetylmuramate; Undecaprenyl‐PP (Und‐PP), di‐trans, poly‐cis‐undecaprenyl diphosphate; mDAP, meso‐2,6‐diaminopimelate; UDP‐NAM‐Tripeptide, UDP‐NAM‐l‐Ala‐d‐Glu‐mDAP; UDP‐NAM‐Pentapeptide, UDP‐NAM‐l‐Ala‐d‐Glu‐mDAP‐d‐Ala‐d‐Ala; Lipid I, Und‐PP‐NAM‐l‐Ala‐d‐Glu‐mDAP‐d‐Ala‐d‐Ala; Lipid II, Und‐PP‐NAM‐(GlcNAc)‐l‐Ala‐d‐Glu‐mDAP‐d‐Ala‐d‐Ala; DAT, d‐alanine transaminase; PGPase, phosphatidylglycerophosphatase.
