Figure 7.
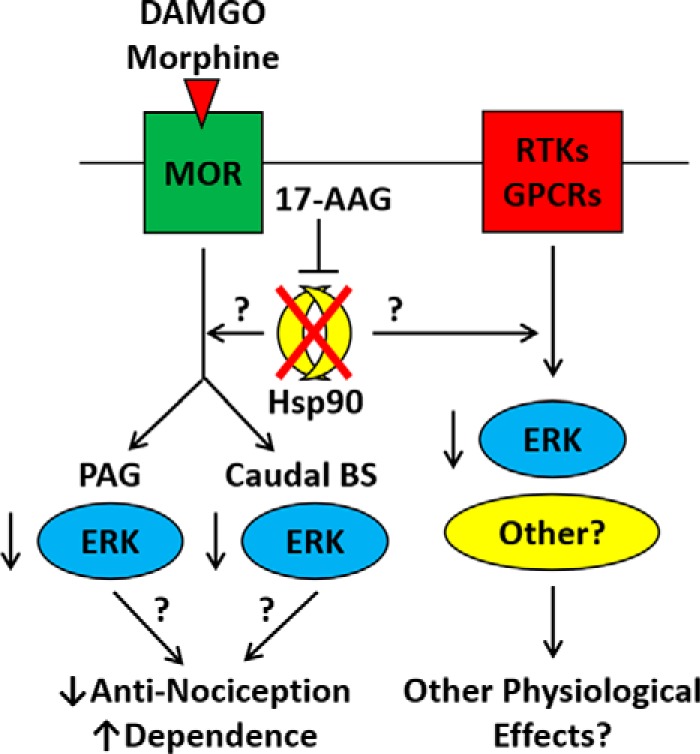
Summary model of the role of Hsp90 in opioid signaling and behavior. This model summarizes our findings that Hsp90 inhibition causes ERK MAPK to lose the ability to be stimulated through opioid-receptor activation in the brain. This loss of stimulation may account for the loss of opioid anti-nociception seen in three pain models. The molecular mechanisms linking Hsp90 to ERK and ERK to anti-nociception and potentially to dependence/withdrawal are currently unknown. We also note in this figure that Hsp90 effects on signaling kinases are likely to impact other receptor systems, including GPCRs and receptor tyrosine kinases. Stimulating these systems while Hsp90 is inhibited could cause a variety of other physiological effects.
