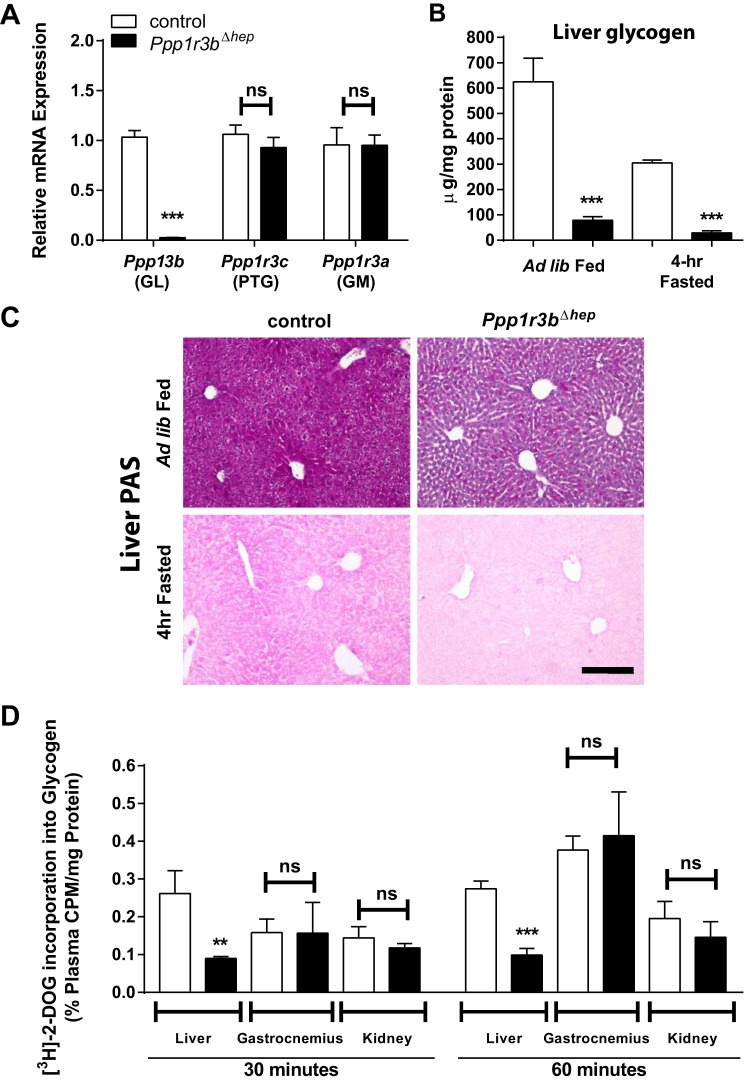
Figure 1.
Liver-specific deletion of Ppp1r3b results in depletion of hepatic glycogen content. A, hepatic mRNA levels of Ppp1r3a, Ppp1r3b, and Ppp1r3c measured by SYBR-Green RT quantitative PCR in control and Ppp1r3bΔhep [Alb-Cre] mice (n = 10–14/genotype). B, hepatic glycogen content in ad libitum chow-fed and 4-h fasted control and Ppp1r3bΔhep mice (n = 6/genotype). C, PAS staining of paraffin-embedded liver sections from ad lib fed and 4-h fasted Ppp1r3bΔhep and control mice shows depletion of glycogen (purple stain). Note that the 4-h fasted sections were not counterstained with hemotoxylin. Scale bar, 1 mm. D, 2-deoxy-d-[3H] glucose (2-DOG) incorporation into glycogen was measured after 6 h of fasting in control and Ppp1r3bΔhep mice (n = 3–4/genotype). Label incorporation was measured as cpm from precipitated glycogen from tissue lysates and normalized to plasma cpm/mg protein. The results were replicated in at least two independent experiments. All mice were adults (2–8 months) and were age-matched within experiments. The data are expressed as the means ± S.E. Significance was determined in all panels by unpaired Student's t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0001. ns, not significant.