Figure 15.
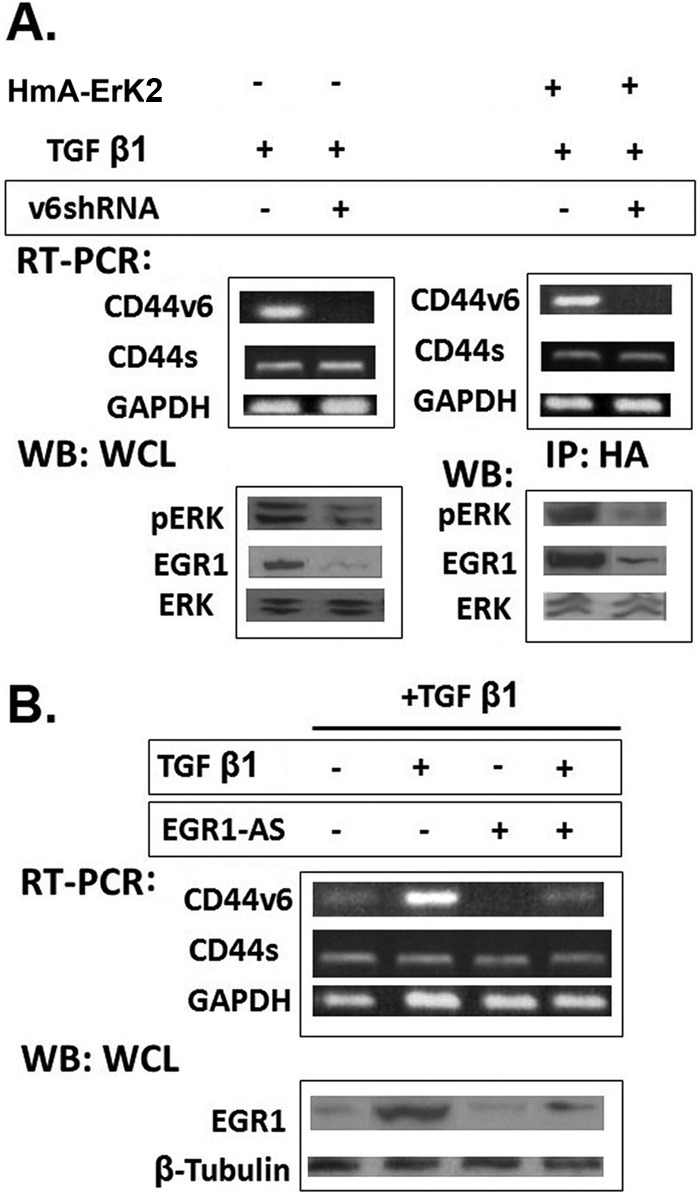
shRNA-mediated knockdown of CD44V6 down-regulates ERK induced EGR-1 activity. A (left), RT-PCR analyses of CD44V6 in HNLFbs transfected with control shRNA or CD44V6 shRNA followed by TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) stimulation for 24 h. GAPDH was used as a loading control. WB analyses of ERK phosphorylation following TGFβ1 (2.5 ng/ml) stimulation for 16 h in cells transfected with control or CD44V6 shRNA were done with antibodies recognizing pERK, EGR1, or total ERK. Right, RT-PCR analyses are shown for CD44v6 in HNLFbs transfected with control shRNA or CD44v6 shRNA or treated with 10 μm U0126 for 2 h or with an additional hemagglutinin (HmA-ERK2) construct, followed by TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) stimulation for 24 h. Immunoprecipitation with HmA antibody was followed by WB analyses for pERK, ERK, and EGR1. B, RT-PCR analyses of CD44V6 and Western blot analyses of EGR1 expression are shown for HNLFbs that were stimulated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 24 h in the absence or presence of EGR-AS nucleotides. Data are representative of three (n = 3) independent experiments.
