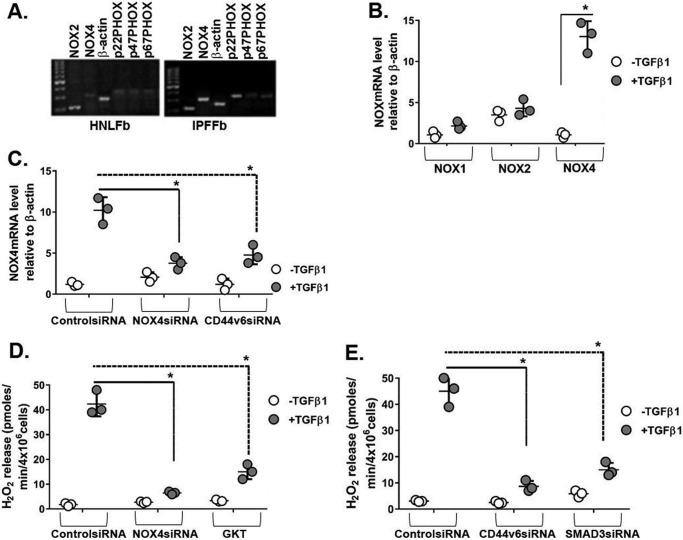
Figure 1.
NOX4 is induced during the fibrogenic phase of IPF, and CD44V6 regulates both NOX4 expression and NOX4-mediated H2O2. A, mRNA expressions of NOX components are shown in HNLFbs and IPFFbs. B, mRNA expressions by real-time PCR for NOX1, NOX2, and NOX4 in NLFbs treated with or without TGFβ1 and expressed relative to β-actin. C, effects of control siRNA, NOX4 siRNA, and CD44V6 siRNA on NOX4 mRNA expression in HLFbs treated with or without TGFβ1 are shown and expressed relative to β-actin. D, effects of inhibiting NOX4 by NOX4-specific siRNA or by pharmacologic inhibitor GKT137831 (1 μm) on extracellular release of H2O2 by HLFbs treated with or without 2.5 ng/ml TGFβ1 for 48 h. E, effects of blocking CD44V6 and SMAD3 using specific siRNAs on extracellular release of H2O2 by HNLFbs treated with or without 2.5 ng/ml of TGFβ1 for 48 h. The data in A are representative of three independent experiments. The experimental data in B–E are from three sets of HNLFbs with three independent experiments and are expressed as means ± S.D. (error bars). Statistical analysis was with ANOVA (B, *, p ≤ 0.005 versus TGFβ1-untreated control group; C, *, p ≤ 0.01 versus TGFβ1-treated control shRNA group; D and E, *, p ≤ 0.01 versus TGFβ1-treated control siRNA group).