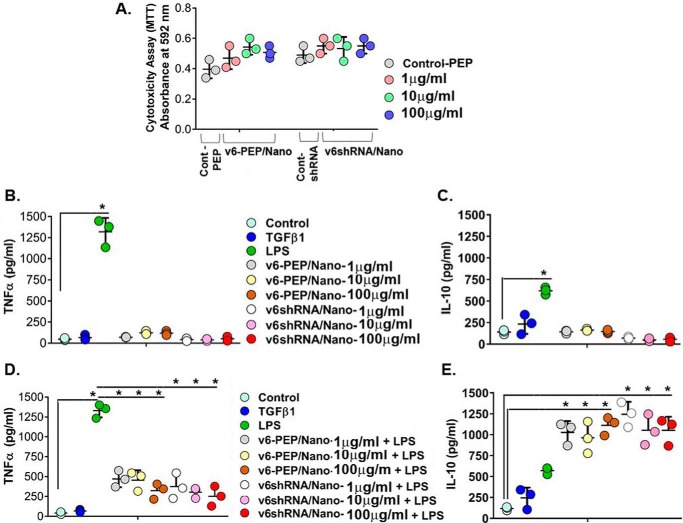
Figure 11.
The CD44V6 shRNA (V6 shRNA) and the V6-PEP/nanoparticles are non-cytotoxic and mediate anti-inflammatory responses. A, cytotoxicity analysis (by MTT assay) results are shown for V6 shRNA/nanoparticles and V6-PEP/nanoparticles in PBMCs (leukocytes). The V6 shRNA/nanoparticle (pSico-CD44V6 shRNA/Tf-PEG-PEI plus FSP-1-Cre/Tf-PEG-PEI) and v6-PEP/nanoparticle (1–100 μg/ml) showed no statistical difference when compared with control (PBMCs with control peptide treatment; the data of other control (PBMCs with control shRNA/nanoparticle (pSico-scrambled shRNA/Tf-PEG-PEI plus FSP-1-Cre/Tf-PEG-PEI) treatment) show the same cytotoxicity as PBMCs with control peptide treatment (data not shown)), indicating that the tested concentrations did not have a cytotoxic effect. B–E, analyses of cytokine production by PBMCs after stimulation for 24 h. Analyses of pro-inflammatory TNF-α (B) and regulatory IL-10 (C) cytokines released in the absence of inflammatory stimulus are shown. Analysis of TNF-α (D) and IL-10 (E) cytokines released after PBMC stimulation with 1 μg/ml LPS are shown. PBMC cultures pretreated with the V6-PEP/nanoparticle or with V6 shRNA/nanoparticle at 1 μg/ml were able to decrease TNF-α production (*, p < 0.001). PBMC cultures pretreated with the V6-PEP/nanoparticle or with V6 shRNA/nanoparticle followed by stimulation with 1 μg/ml LPS resulted in a significant increase in IL-10 production when compared with control (± S.D.; n = 3; *, p ≤ 0.001).