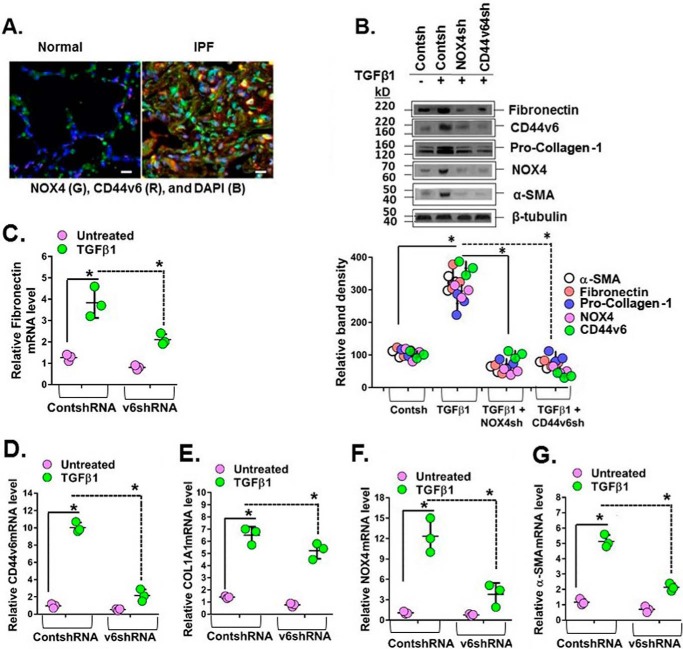
Figure 5.
CD44v6 and NOX4 expression are increased in lung sections of human subjects with IPF, and they mediate profibrotic protein expression in IPFFbs. A, immunohistochemical staining shows increased expression of NOX4 and CD44v6 in inflammatory cells comparing sections from a representative IPF patient lung and a normal lung. B–G, total cell lysates were examined by Western blot analysis for the indicated protein expressed relative to β-tubulin. The data in the experiments in B are from three sets of IPFFbs with three independent experiments. The densitometry results, expressed as the means ± S.D. (error bars) obtained for representative Western blots of the indicated proteins in C–G, are shown in the top panel of B. The effects of shRNA-mediated knockdown of NOX4 in IPFFbs treated with or without TGFβ1 (2 ng/ml) on the expression of α-SMA mRNA (C) and protein (B), on fibronectin mRNA (D) and protein (B), on COL1A1 mRNA (E) and protein (B), on NOX-4 mRNA (F) and protein (B), and on CD44v6 mRNA (G) and protein (B) were determined by real-time PCR (quantified relative to β-actin at 24 h) and by Western immunoblotting (at 72 h) after TGFβ1 treatment. The densitometry results obtained for Western blotting of the proteins are shown in the bottom panel of B. The experimental data in B–G are from three sets of IPFFbs with three independent experiments and are expressed as the means ± S.D. Statistical analysis was with ANOVA (B, *, p ≤ 0.005 versus control shRNA-transfected group; C–G, *, p ≤ 0.01 versus control shRNA-transfected group).