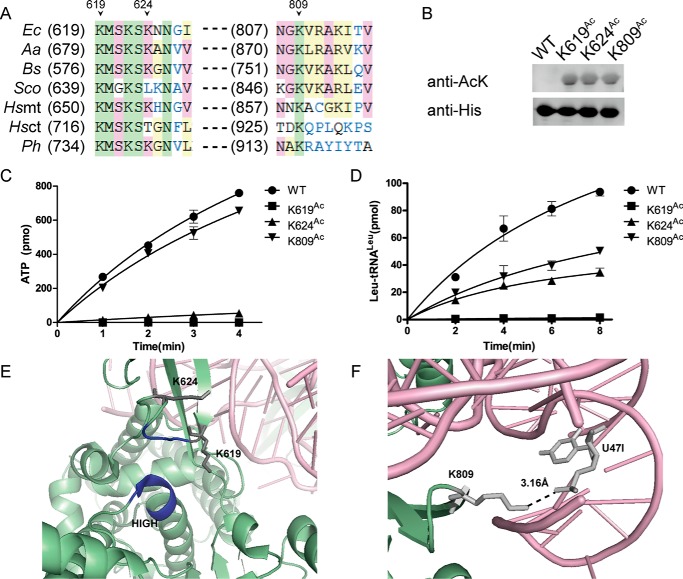
Figure 4.
Effect of acetylation of Lys residues on the Leu activation and aminoacylation activities of EcLeuRS. A, sequence alignment of LeuRSs from various species in regions homologous to Lys619, Lys624, and Lys809 in EcLeuRS. Ec, E. coli; Aa, Aquifex aeolicus; Bs, B. subtilis; Sco, Streptomyces coelicolor; Hs, H. sapiens; Ph, Pyrococcus horikoshii; mt, mitochondrial; ct, cytoplasmic. B, Western blotting confirming the incorporation of AcK in EcLeuRS-K619Ac, EcLeuRS-K624Ac, and EcLeuRS-K809Ac. C, Leu activation of EcLeuRS-K619Ac, EcLeuRS-K624Ac, and EcLeuRS-K809Ac. D, aminoacylation of EcLeuRS-K619Ac, EcLeuRS-K624Ac, and EcLeuRS-K809Ac resembling that of the K-Q mutants. E, closer view of the orientation of Lys619 and Lys624 relative to the conserved HIGH and KMSK motifs (HMGH and KMSK in EcLeuRS, depicted in dark blue; PDB code 4ARC). F, closer view of the interaction between EcLeuRS Lys809 and EctRNALeu U47I (PDB code 4ARC). The results are the averages and standard deviations from three independent experiments, and all Western blots were repeated.