Figure 1.
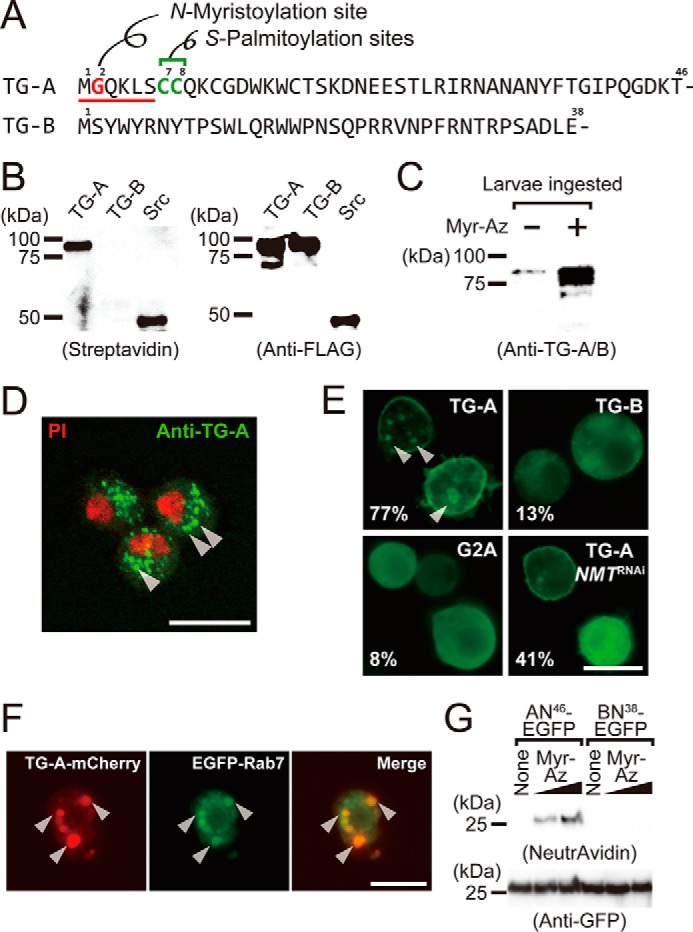
TG-A is a target for N-myristoylation. A, the N-terminal sequences of TG-A and TG-B. The N-myristoyl consensus sequence is underlined, and the N-myristoylated glycine residue and the S-palmitoylation sites are shown in red and green, respectively. B, the N-myristoylated proteins were detected by streptavidin blotting (left) and the expressed proteins were checked by Western blotting using the anti-FLAG antibody (right). C, third instar larvae (w1118) ingested myristic acid-azide and the resulting N-myristoylated proteins were labeled with biotin. Proteins purified on avidin-immobilized agarose were analyzed by Western blotting using the anti-TG-A/B antibody. D, hemocytes of third instar larvae were analyzed by immunocytochemistry using the anti-TG-A-specific antibody (green). PI, propidium iodide (red). Arrowheads indicate puncta structures. The scale bar in white is 10 μm. E, Drosophila S2 cells expressing TG-A, TG-B, or G2A tagged with the C-terminal V5-His6 tag were analyzed by immunocytochemistry using the anti-His6 tag antibody. The percentages of cells with the plasma membrane-localized signal are shown (n = 300). Arrowheads indicate puncta structures. The scale bar in white is 10 μm. F, S2 cells were co-transfected with the C-terminal mCherry (red)-tagged TG-A and the N-terminal EGFP (green)-tagged Rab7 and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. G, S2 cells expressing AN46-EGFP and BN38-EGFP were incubated with myristic acid-azide (8 or 80 μm) and analog-incorporated proteins were labeled with biotin alkyne using click chemistry. The resulting proteins were purified using anti-GFP-agarose, and detected using NeutrAvidin-horseradish peroxidase. Myr-Az, myristic acid-azide.
