Figure 7.
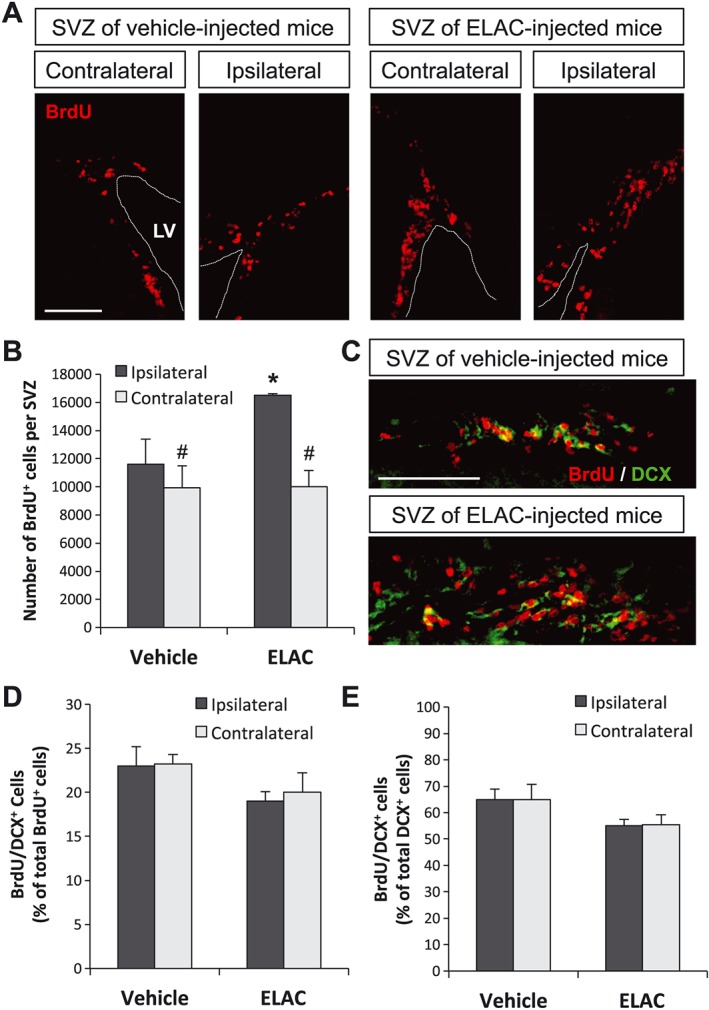
Effect of in vivo administration of ELAC on SVZ neurogenesis. Adult mice were injected in the right lateral ventricles with ELAC (5 μM, 2 μL; n = 6) or vehicle (n = 6) and then daily injected with the cell‐division marker BrdU (120 mg·kg−1) for 3 days. (A) Fluorescence microscopy images of brain coronal sections showing the ipsilateral and contralateral SVZs of mice treated with ELAC or vehicle; sections were processed for immunohistochemical detection of BrdU+ nuclei (red). (B) Quantification of BrdU+ cells within the SVZ of mice that had received i.c.v. injections of ELAC or vehicle. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images showing a close‐up of the laterodorsal corner of ELAC‐ or vehicle‐injected (ipsilateral) SVZs; BrdU (red) and the early neuronal marker DCX (green) were detected by immunohistochemistry. (D) Quantification of the percentage of BrdU+ cells that co‐express the early neuronal marker DCX. (E) Quantification of the percentage of DCX+ cells that co‐express BrdU. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 6 animals per condition. *P < 0.05 when comparing ELAC‐ with vehicle‐injected SVZs in a one‐way ANOVA test; #P < 0.05 when comparing ipsilateral and contralateral SVZs within the same animal group in a Student's t‐test for paired samples. Abbreviations: LV, lateral ventricle. Scale bar: 100 μm.
