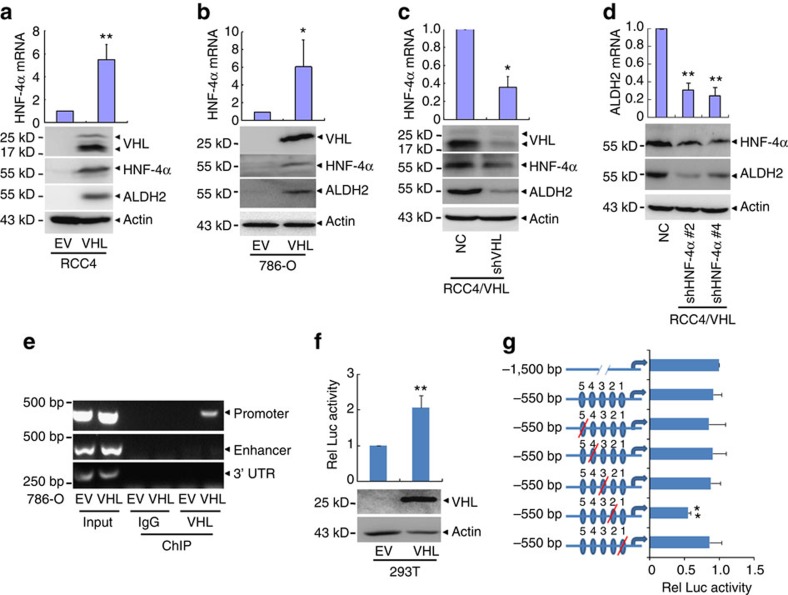
Figure 7. VHL regulates ALDH2 expression through HNF-4α.
(a–c) The mRNA and protein levels of the indicated genes were detected by real-time quantitative PCR with reverse transcription (RT–PCR) and Western blot respectively. (d) RCC4/VHL cells were stably transfected with shRNAs against HNF-4α (#2 and #4), the mRNA and protein levels of the indicated genes were detected. (e) VHL binding to HNF-4α promoter or enhancer was analysed by chromatin immunoprecipitation in 786-O/EV and 786-O/VHL cells. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated with IgG or anti-VHL antibody and analysed by PCR using primers indicated above. (f) 293T cells were transfected with luciferase reporter plasmids driven by HNF-4α promoter together with or without VHL expression vector for 36 h, then detected the relative luciferase activity. Protein levels of VHL were detected by western blot with actin as a loading control (low panel). (g) Luciferase reporter plasmids driven by trunk or mutated sequences as indicated were transfected together with VHL-expressing vector or empty vector into 293T cells for 36 h. All the relative luciferase activities of HNF-4α promoter were normalized by pSV40-Renilla and estimated as the relative folds against cells. Blue ovals represent potential-binding sites. Arrows represent the transcriptional start point of HNF-4α. Columns, means of three independent experiments; bars, s.d. (*P<0.05,**P<0.01 for t-test).