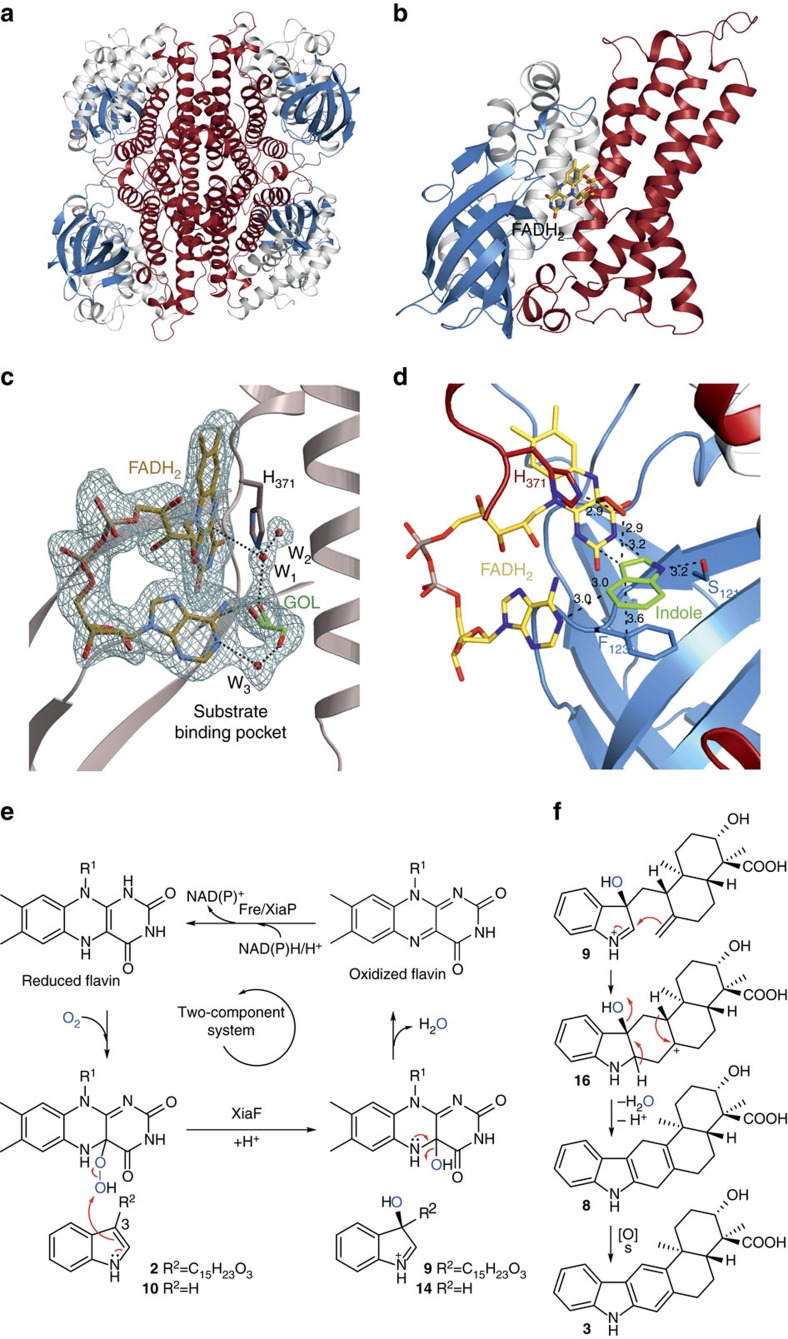
Figure 5. Structural analysis of XiaF and scheme of FADH2-mediated indole hydroxylation.
(a) Ribbon structure of the homotetramer (PDB entry code: 5LVU). (b) Close-up cartoon representation of a monomer with bound FADH2 (PDB entry code: 5LVW) The N-terminal domain is coloured in white, the β-sheet domain in blue and the C-terminal domain in red. (c) Ribbon diagram of XiaF with the enlarged active site. The electron density represents a 2FO-FC map with the displayed FADH2, glycerol (GOL) and three water molecules (W1-3) omitted for phasing (PDB ID: 5MR6). The amino acid is labelled by the one-letter code and numbered according to the XiaF sequence. Black dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. (d) Docking of indole (carbon atoms coloured in green), using AutoDock Vina50, with XiaF in complex with the modelled reaction intermediate FAD–OOH. Distances in Å. (e) Catalytic cycle of XiaF consuming one molecule of oxygen and of reduced flavin provided by cognate reductase, yielding a C-3-hydroxylated indole derivative. The oxidized cofactor is transferred back to the reductase where it is recycled in a NAD(P)H/H+-dependent reaction. (f) Nucleophilic attack of the exo-methylene group on 3-hydroxyiminium cation 9 results in the pentacyclic intermediate 16. Deprotonation and loss of an equivalent of water yields prexiamycin (8), which aromatizes to yield 3. Spontaneous reactions are indicated by ‘s’.