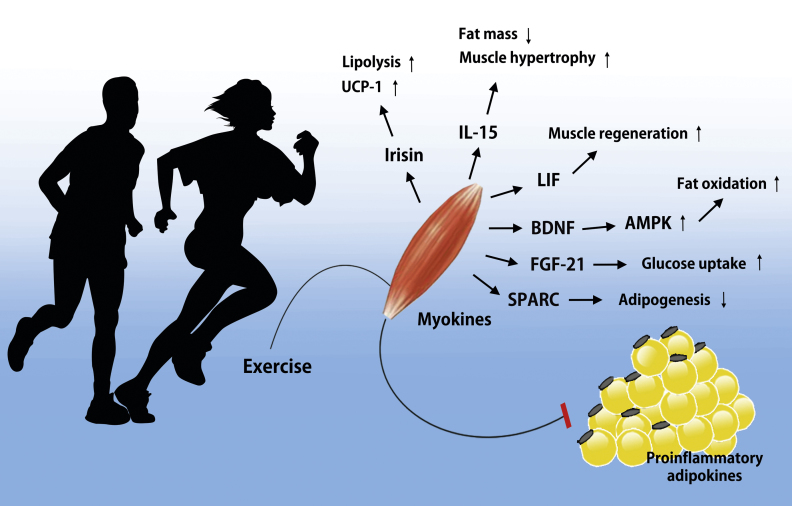
Fig. 1.
Potential role of exercise-induced myokines. Skeletal muscle expresses and releases myokines into the circulation. Especially under conditions of metabolic diseases including obesity and diabetes, adipose tissue secretes proinflammatory adipokines that promote pathological processes such as atherosclerosis and insulin resistance. However, exercise-induced myokines may balance and counteract the effect of adipokines. In response to muscle contraction following exercise, muscle fibers express myokines such as irisin, IL-15, LIF, BDNF, FGF-21, and SPARC, which subsequently exert their effects locally within the muscle or their target organs.
AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; FGF-21, fibroblast growth factor 21; IL, interleukin; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; UCP-1, uncoupling protein 1.